Much like Pandas the Numpy library is massive. Numpy is mostly used to work with arrays. Numpy arrays are much like Python lists or Pandas dataframes. They all kind of relate to each other. But there are differences between them in terms of speed, memory usage, and rules. Numpy arrays are generally faster than python lists and allow for more flexiblity in terms of memory useage. Most of the methods I include here will pertain to array creation, access, and manipulation.
Basic rules and structure of Numpy arrays:
Basic numpy array rules:
- all the data items in an array must be homogenous (same data type)
- "ndarray" is synonymous with "array"
- when reshaping an array the dimensions must be a product of the size
- a vector is an array with a single dimension—there’s no difference between row and column vectors
- the shape of an array is a tuple of non negative integers
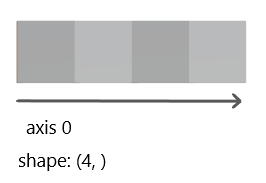
- array shape (axis_0,) a 1-dimensional array
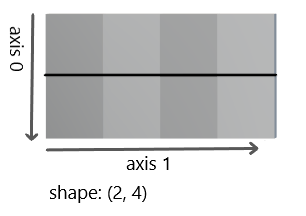
- array shape (axis_0, axis_1) a 2-dimensional array
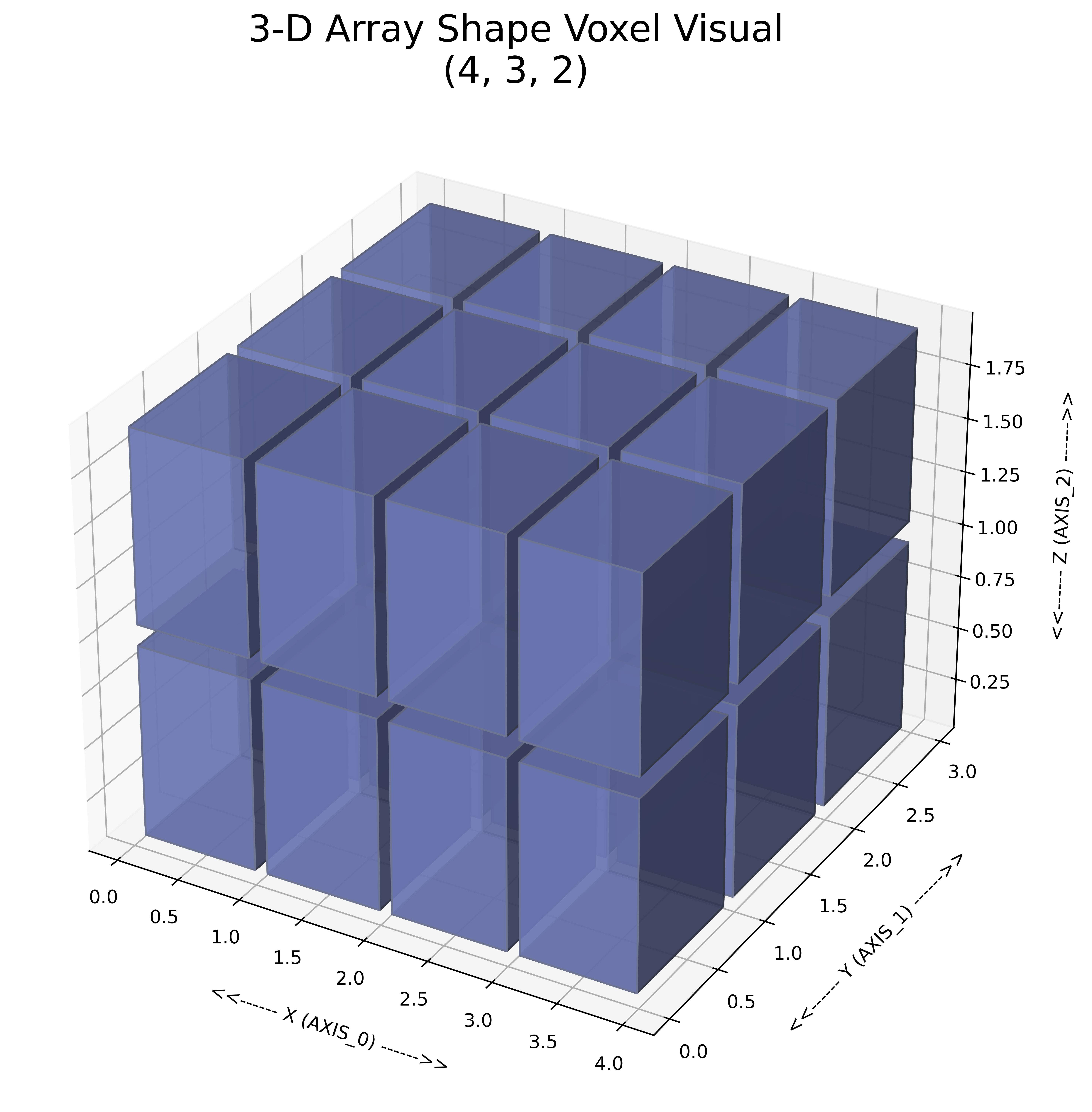
- array shape (axis_0, axis_1, axis_2) a 3-dimensional array
Arrays shapes visualized:
'''
Here is a 1d array visualized...
'''
In[]: one_d_array = np.arange(0, 4) ; print(one_d_array)
Out[]: [0 1 2 3]
In[]: two_d_array = np.arange(0, 8)
In[]: two_d_array = two_d_array.reshape(2, 4) ; print(two_d_array)
Out[]:
[[0 1 2 3]
[4 5 6 7]]
#
In[]: three_d_array = np.arange(0, 24).reshape(4,3,2)
In[]: three_d_array
Out[]:
[[[ 0 1]
[ 2 3]
[ 4 5]]
[[ 6 7]
[ 8 9]
[10 11]]
[[12 13]
[14 15]
[16 17]]
[[18 19]
[20 21]
[22 23]]]
Basic Structures of Numpy Arrays:
One-dimensional array
'''
A 1-dimensional array is just like a Python list.
'''
In[]: a_1 = np.array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
In[]: a_1
Out[]: array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
In[]: a_1.ndim #calls the number of dimensions
Out[]: 1
Two-dimensional array
'''
A 2-dimensional array
'''
#the square extra brackets [] add a dimension
In[]: a_1 = np.array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
In[]: a_1
Out[]: array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
In[]: a_2.ndim
Out[]: 2
'''
Two dimensional arrays can also look like the following.
'''
In[]: a_2_1 = np.array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
In[]: a_2_1
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
Three-dimensional arrays
'''
A Three-dimensional array
'''
In[]: a_3 = np.array([[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]]])
In[]: a_3
Out[]: array([[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]]])
'''
Three dimensional arrays can also look like the following
'''
In[]: a_3_1 = array([[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]]])
In[]: a_3_1
Out[]:
array([[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]]])
Note that numpy arrays are not limited to three dimensions. You can really use whatever you need.
Shape, Size, and N-dimensions
There are three built in functions in Numpy that return the shape, size, and number of dimensions of an array. They will be useful for exploring an arrays basic structure—particularly when dealing with very large arrays that are not visually intuitive.
'''
Here is an array we are going to look at.
'''
In[]: a_3_1 = np.array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15]]])
In[]: a_3_1.shape
Out[]: (1, 5, 3)
In[]: a_3_1.size
Out[]: 15
In[]: a_3_1.ndim
Out[]: 3
Creating Arrays
Creating arrays can be very simple or complex depending on what the user is trying to accomplish. This is not a full showing of examples but I have included some interesting methods of array creation.
Basic array creation:
'''
Creating numpy arrays for whatever purpose is somewhat easy.
Here are a few methods to do so almost exactly like using Python's
built in range() function.
'''
#create a numpy array using np.arange()
In[]: np.arange(0, 10)
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In[]: np.arange(0, 10, 2)
Out[]: array([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
In[]: np.arange(5, 15)
Out[]: array([ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14])
In[]: np.arange(5, 15, dtype=float)
Out[]: array([ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14.])
Generate arrays of zeros or ones:
'''
This can be an effective method of generating arrays composed
purly of zeros or ones.
'''
In[]: np.zeros(10)
Out[]: array([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
In[]: np.zeros([2,5])
Out[]:
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
In[]: np.zeros([2,5,6])
Out[]:
array([[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]])
#the same syntax is used for arrays created purly of ones
In[]: np.ones(10)
Out[]: array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
In[]: np.ones([2,5])
Out[]:
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
In[]: np.ones([2,5,6])
Out[]:
array([[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]],
[[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]])
Create an array of evenly spaced numeric data:
'''
This is an interesting exersize that returns evenly spaced
numeric data in a specific array length.
'''
In[]: np.linspace(1, 10, num=10)
Out[]: array([ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.])
In[]: np.linspace(0, 10, num=5)
Out[]: array([ 0. , 2.5, 5. , 7.5, 10. ])
In[]: np.linspace(0, 1, num=5)
Out[]: array([0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])
Reshaping Arrays
When you reshape an array the axes must be a product of the array size. So, you can find all the possible shapes of an array by taking the factors of the array size, select pairs or duos depending on target dimensions, and then re-ordering them into a new compatible shape.
Basics of Reshaping an array:
'''
Here we have a 1-d array of the size 12
'''
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 12)
In[]: a_4
Out[]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])
'''
There are multiple combinations to reshape this array into a 2-d, 3-d or more array.
But in order for the shape to be compatible all the axes must be a product of 12.
To do this you must first find all the factors of 12. A factor is a number that divides
evenly into the target number.
This looks like the following:
'''
#This loop returns the factors of 12
In[]: for i in range(1, 12 + 1):
if 12 % i == 0:
print(i, end=', ')
Out[]: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12,
'''
Now that we have the factors of 12 we can better see how
to reshape the array of size 12. Let's reshape the array to
2-dimensions (2, 6). This is compatible because the product of
2 and 6 is 12.
'''
In[]: a_4.reshape(2, 6)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]])
'''
We could also reshape the array to 2-dimensions with reversed axes
'''
In[]: a_4.reshape(6, 2)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1],
[ 2, 3],
[ 4, 5],
[ 6, 7],
[ 8, 9],
[10, 11]])
'''
So notice that the order does not matter as long as the axes
are a product of 12. Here again is a 2-dimensional array with
3 and 4.
'''
In[]: a_4.reshape(3, 4)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
In[]: a_4.reshape(4, 3)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
'''
Now reshape a_4 to 3-dimensions
'''
In[]: a_4.reshape(6,1,2)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1]],
[[ 2, 3]],
[[ 4, 5]],
[[ 6, 7]],
[[ 8, 9]],
[[10, 11]]])
In[]: a_4.reshape(2,1,6)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]],
[[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]])
'''
To make a_4 a four-dimensional array add a 1 somewhere in the axes.
'''
In[]: a_4.reshape(1,2,1,6)
Out[]:
array([[[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]],
[[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]]])
#or...
In[]: a_4.reshape(1,1,3,4)
Out[]:
array([[[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]]]])
Getting all the possible axes combinations of an array based on its size
and a given dimension can start to get a little intense—particularly when
dealing with larger numbers.
I put some effort trying to find a method that; given a size and dimension
the output would be all/most possible combinations where the numbers are the
product of the size. Not easy to do for say a number like 100,000.
For a number like 12 this task is a little easier because it is smaller. All of
the possible shapes for an array of size 12 in 1, 2, and 3 dimensions barring adding
ones are:
[(12,)]
[(1, 12), (2, 6), (3, 4)]
[(1, 2, 6), (1, 3, 4)]
Each of the above tuples—within a list—represent a combination of axes that can
reshape the array of size 12. You may notice you could also reshape the array
to (1, 1, 12) but that is rather intuitive so I did not include it.
So, how can we do this without having to manually get the factors of a number,
and then get all the factor pairs or trios that are products of that number
depending on our target number of dimentions? I personally couldn't find a method
that someone else had pre-written to do this.
I came to the conclusion that I had to write one myself. Directly below is my reshape calculator:
Array Reshape Calculator
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ANG Array Reshape Calculator
"""
import numpy as np
import itertools
import functools as f_tools
import warnings
def reshape_calc(size, n_dims=2, **kwargs):
"""
reshape_calc(size = IntegerSizeOfAnArray, n_dims=NumberOfDimensions)
Returns all posible shapes of a given array from array size factors defaulted to 2 dimensions.
Any of the returned tuples can be re-ordered to fit array needs and will work in reshaping.
"""
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=RuntimeWarning)
escape_1 = None
if n_dims == 0:
print("\nn_dims cannot equal zero.")
return None
f_lst = []
shapes_actual = []
shapes_actual_all = []
escape_question = False
is_prime = False
n_dims_proxy = n_dims
tup_list_lengths_proxy = False
#####CREATE FACTOR LIST#####
for i in range(1, size + 1):
if size % i == 0:
f_lst.append(i)
#####IDENTIFY IF SIZE IS PRIME#####
if len(f_lst) == 2:
print(size, "is a prime number.\n\nThe only possible shape is, one to any number of ones and itself—limited only by memory.")
is_prime = True
#####IDENTIFY IF SIZE FACTORS LIST IS LARGE#####
if ((len(f_lst) > 45) & (n_dims > 6)):
print("The number input for the array size has more than 45 factors and n_dim called is greater than 6.")
print("This could cause the runtime of this program to increase by several minutes.")
escape_1 = input("Are you sure you want to continue [y] [n]: ")
escape_question = True
escape_options = ["y","n"]
if escape_1 not in escape_options and (escape_question == True):
print('Input must be "y" or "n"')
elif escape_1 == "n":
print("\nExecution Aborted")
return None
elif escape_1 == "y":
print("This may take several minutes...")
#####TURN FACTORS LIST TO ARRAY#####
f_arr = np.asarray(f_lst, dtype=np.int64)
#####TAKE THE DESIRED N_DIMS AND ALL THE PRODUCTS OF FACTORS THAT EQUAL THE SPECIFIED SIZE#####
for i in range(n_dims):
for i in np.arange(n_dims, n_dims+1, dtype=np.int64):
combinations = itertools.combinations(f_arr, i)
for i in combinations:
if f_tools.reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, i, 1) == size:
shapes_actual_all.append(i)
n_dims -= 1
print("\nThe factors of",size,"are:", f_lst,"\n")
print("All possible shapes (which can be re-ordered) given the size and n_dims specified:\n")
#####IF THE SIZE IS PRIME RETURN ONES AND SIZE#####
#####ELIF THE SIZE IS NOT PRIME RETURN ALL SIZES PADDED BASED ON N_DIMS SPECIFIED#####
if is_prime == True:
new_shape = np.ones(n_dims_proxy-1, dtype=int)
new_shape_lst = [i for i in new_shape]
new_shape_lst.append(size)
new_shape_lst = tuple(new_shape_lst)
shapes_actual_all.append(new_shape_lst)
for i in shapes_actual_all:
if len(i) == n_dims_proxy:
shapes_actual.append(i)
return shapes_actual
for i in shapes_actual_all:
if len(i) == n_dims_proxy:
shapes_actual.append(i)
if len(shapes_actual) == 0:
tup_list = [list(i) for i in shapes_actual_all]
tup_list_lengths = [len(i) for i in tup_list]
tup_list_lengths_proxy = True
n_dims_padded = []
if tup_list_lengths_proxy == True:
if max(tup_list_lengths) < n_dims_proxy:
for i in shapes_actual_all:
new_shape = np.ones(n_dims_proxy-len(i), dtype=int)
new_shape_lst = list(new_shape)
new_shape_lst.extend(i)
n_dims_padded.append(tuple(new_shape_lst))
n_dims_padded_set = set(n_dims_padded)
n_dims_padded_lst = list(n_dims_padded_set)
return n_dims_padded_lst
fin_return_tup_lst = []
for i in shapes_actual_all:
if len(i) == n_dims_proxy:
fin_return_tup_lst.append(i)
return fin_return_tup_lst
Example use of ANG Reshape Calculator:
'''
With the above I've simplfied the process of viewing all the compatible
axes combinations depending on the desired dimensions.
Say we had a 1-d array that was 150 in size.
'''
In[]: arr_ex = np.arange(0,150)
In[]: arr_ex
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38,
39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,
52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64,
65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77,
78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90,
91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103,
104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116,
117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129,
130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142,
143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149])
'''
Say we need to reshape arr_ex into a 2-dimensional array. What are our options?
'''
In[]: reshape_calc(size=150, n_dims=2)
Out[]:
The factors of 150 are: [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 25, 30, 50, 75, 150]
All possible shapes (which can be re-ordered) given the size and n_dims specified:
[(1, 150), (2, 75), (3, 50), (5, 30), (6, 25), (10, 15)]
'''
The function prints the factors of the size, and then returns a list of tuples
representing the possible reshape axes conditioned on the specified n_dims.
Here is a reshaping of the array:
'''
In[]: arr_ex.reshape(15, 10)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[ 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[ 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[ 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[ 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[ 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[ 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79],
[ 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89],
[ 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99],
[100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109],
[110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119],
[120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129],
[130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139],
[140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149]])
'''
Or, say we wanted to reshape arr_ex to 3 dimensions.
'''
In[]: reshape_calc(size=150, n_dims=3)
Out[]:
The factors of 150 are: [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 25, 30, 50, 75, 150]
All possible shapes (which can be re-ordered) given the size and n_dims specified:
[(1, 2, 75),
(1, 3, 50),
(1, 5, 30),
(1, 6, 25),
(1, 10, 15),
(2, 3, 25),
(2, 5, 15),
(3, 5, 10)]
'''
So we see that (1, 3, 50) is an option. Let's reshape the array where; axis_0 = 3,
axis_1 = 1, and axis_2 = 50
'''
In[]: arr_ex.reshape(3,1,50)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35,
36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47,
48, 49]],
[[ 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61,
62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73,
74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85,
86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97,
98, 99]],
[[100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111,
112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123,
124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135,
136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147,
148, 149]]])
'''
Let's say we wanted to look at all the combinations of the array from the return
for three dimensions. First assign the return to a variable then iterate through
the list.
It's not super practical but it does work so I'll show the last two in the list.
'''
In[]: reshape_out = reshape_calc(size=150, n_dims=3)
In[]: for i in reshape_out[-2:]:
print(str(i),'\n', arr_ex.reshape(i),end="\n\n")
Out[]:
(2, 5, 15)
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]
[ 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29]
[ 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44]
[ 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59]
[ 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74]]
[[ 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89]
[ 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104]
[105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119]
[120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134]
[135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149]]]
(3, 5, 10)
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[ 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19]
[ 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29]
[ 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39]
[ 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49]]
[[ 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59]
[ 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69]
[ 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79]
[ 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89]
[ 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99]]
[[100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109]
[110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119]
[120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129]
[130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139]
[140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149]]]
Reshaping a 3d array visual:
'''
Say we have our 1-d array
'''
In[]: arr_ex = np.arange(0,150)
In[]: arr_ex
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38,
39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,
52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64,
65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77,
78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90,
91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103,
104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116,
117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129,
130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142,
143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149])
Now, let's reshape it to a 3-d array
#
In[]: arr_ex.reshape(1,1,150)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35,
36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47,
48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59,
60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71,
72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83,
84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95,
96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107,
108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119,
120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131,
132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143,
144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149]]])
Visually arr_ex looks something like this:
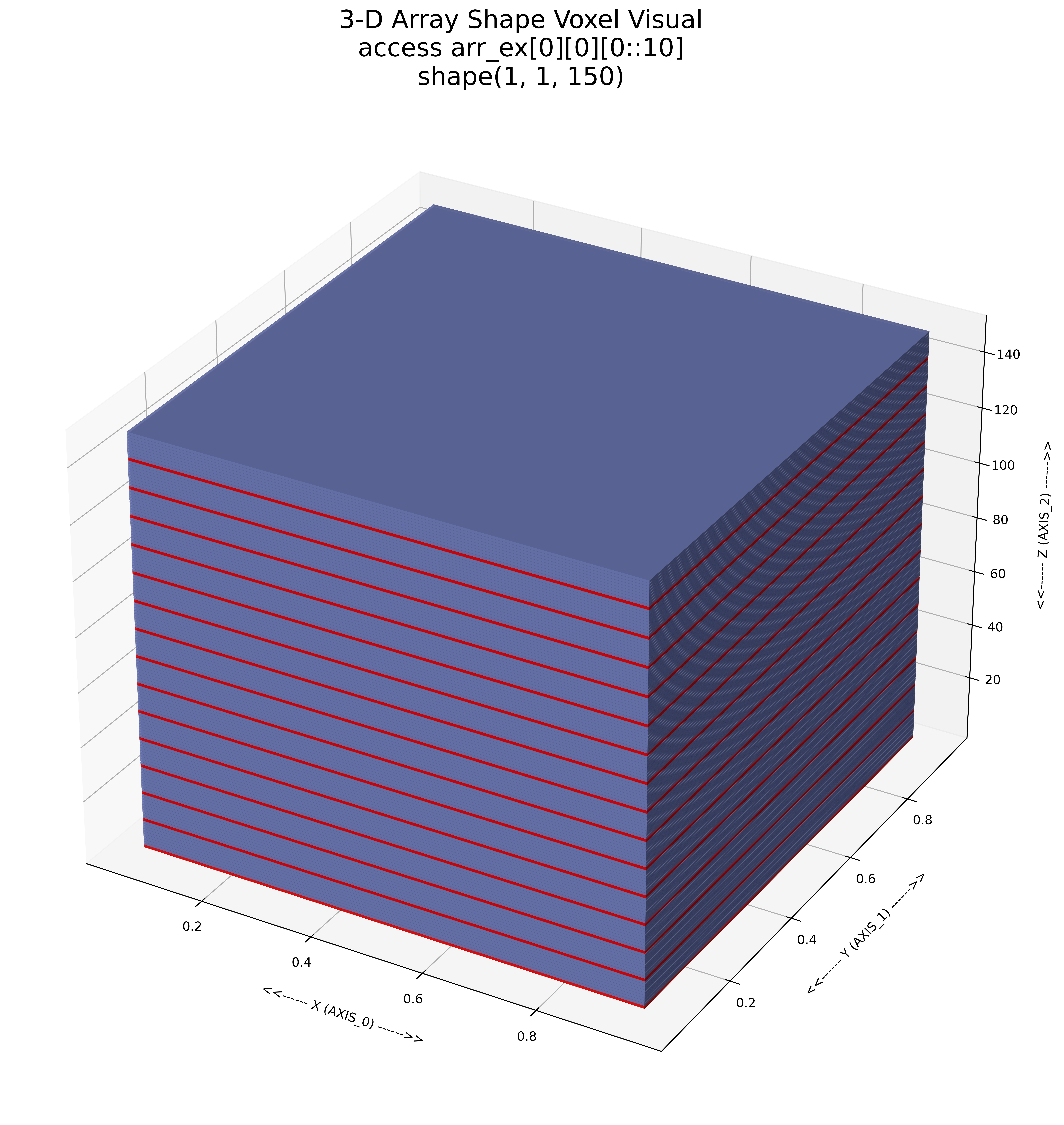
Let's see what it looks like when we reshape this array.
#
In[]: arr_ex = np.arange(0,150).reshape(3,5,10)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[ 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[ 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[ 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[ 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[ 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[ 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79],
[ 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89],
[ 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99]],
[[100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109],
[110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119],
[120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129],
[130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139],
[140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149]]])
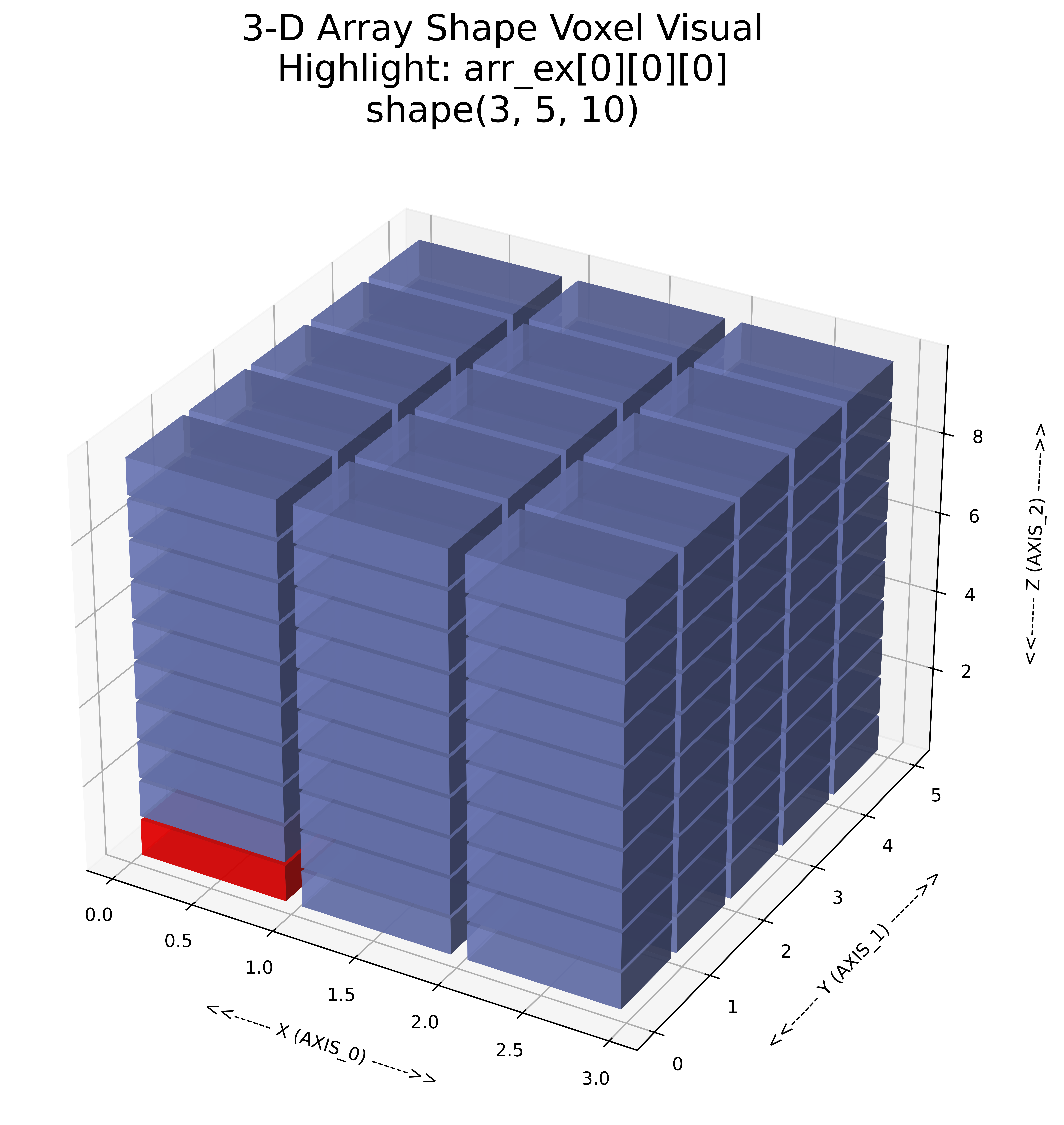
Here's another reshape:
#
In[]: arr_ex = np.arange(0,150).reshape(2,3,25)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24],
[ 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36,
37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48,
49],
[ 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61,
62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73,
74]],
[[ 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86,
87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98,
99],
[100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111,
112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123,
124],
[125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136,
137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148,
149]]])
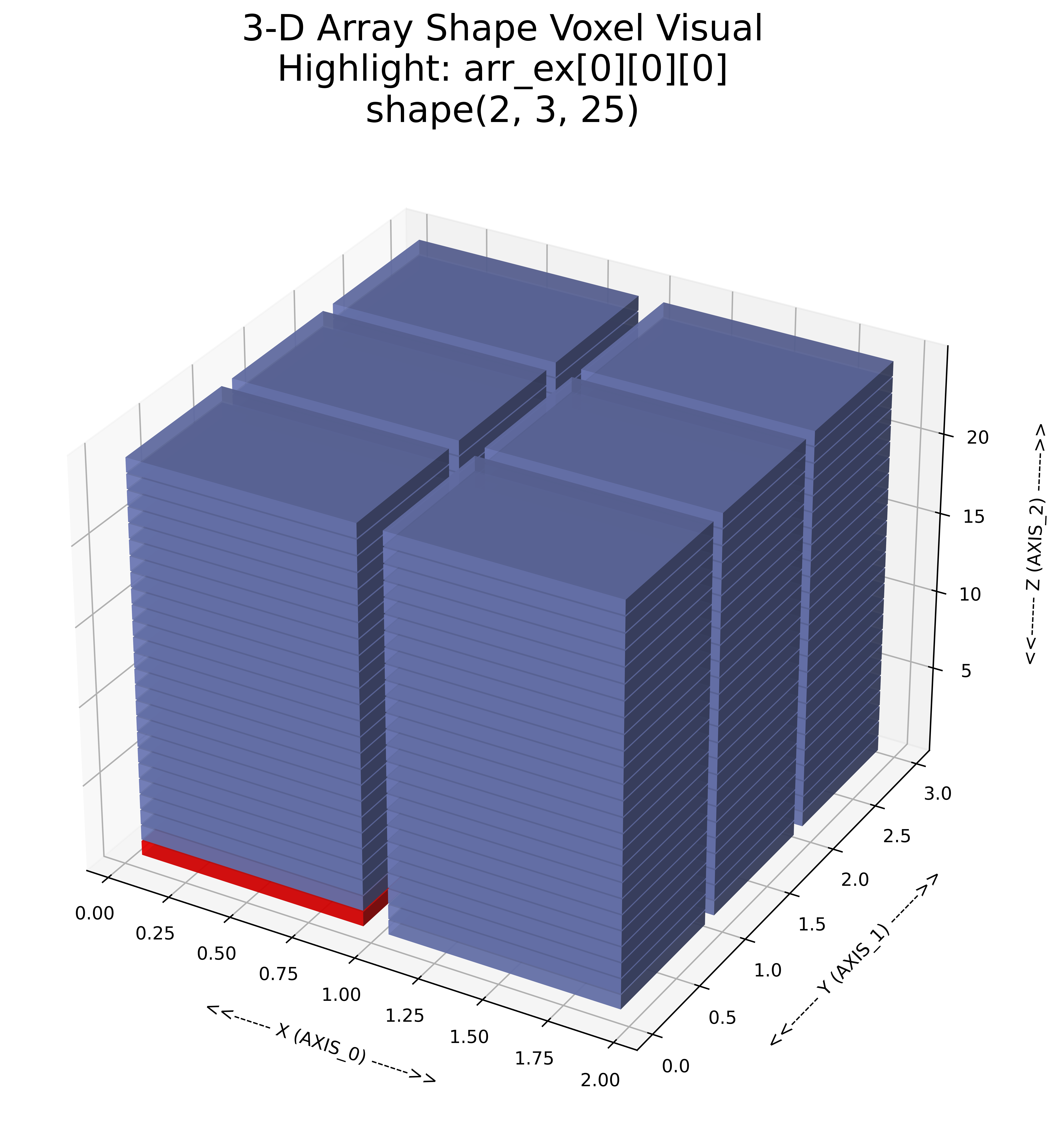
Lastly...
#
In[]: arr_ex = np.arange(0,150).reshape(1, 10, 15)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14],
[ 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29],
[ 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41,
42, 43, 44],
[ 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56,
57, 58, 59],
[ 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71,
72, 73, 74],
[ 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86,
87, 88, 89],
[ 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101,
102, 103, 104],
[105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116,
117, 118, 119],
[120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131,
132, 133, 134],
[135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146,
147, 148, 149]]])
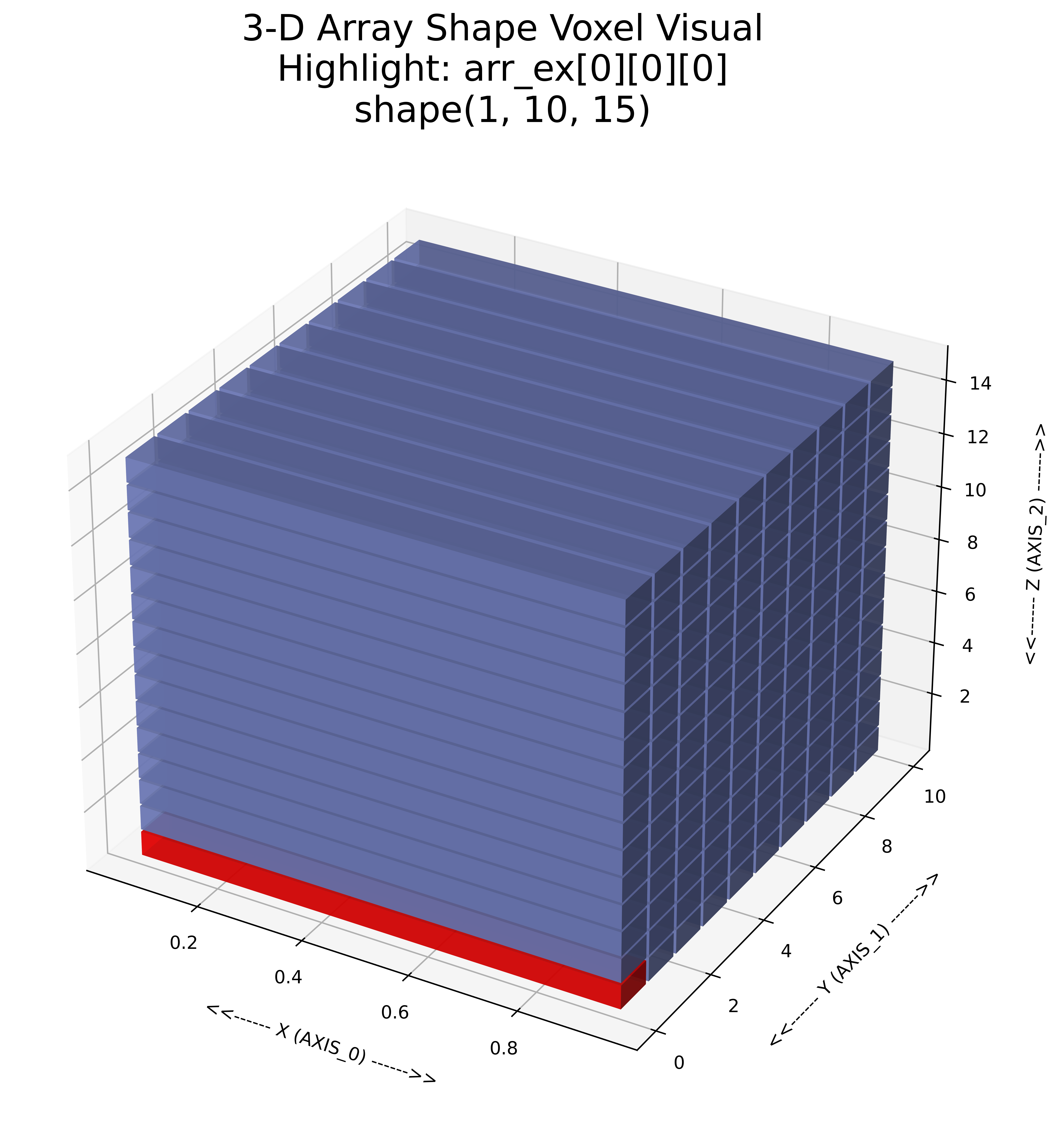
Array Index Slicing
Array index slicing can be very easy for 1-dimensional arrays. It starts to get a little more difficult for 2-dimensional and esspecially 3-dimensional arrays.
Slicing a 1d array:
'''
1d arrays are almost exactly like lists.
'''
In[]: a_1 = np.arange(1, 41) ; print(a_1)
Out[]:
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40]
Visualized a_1 could look something like this:

You can slice a 1-d array almost exactly like a Python list.
'''
Access data with index slicing.
Syntax : SomeArrayObj[start:stop:step]
'''
#Access data at nth index; remember the index starts at 0.
In[]: a_1[0]
Out[]: 1
In[]: a_1[9:20]
Out[]: array([10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20])
#Access data every nth index.
In[]: a_1[1::2]
Out[]: array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40])
In[]: a_1[0::2]
Out[]: array([ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39])
In[]: a_1[9::5]
Out[]: array([10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40])
'''
Access data with an applied comparison operator (1d array)
'''
In[]: a_1[a_1 > 15]
Out[]: array([16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40])
In[]: a_1[(a_1 < 8) & (a_1 > 3)]
Out[]: array([4, 5, 6, 7])
Slicing a 2d array:
Slicing a 2-d array is done similar to a Pandas dataframe.
'''
'''
In[]: a_2 = np.arange(1, 41).reshape(4,10) ; print(a_2)
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
[31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40]])
Visualized a_2 could look something like this:
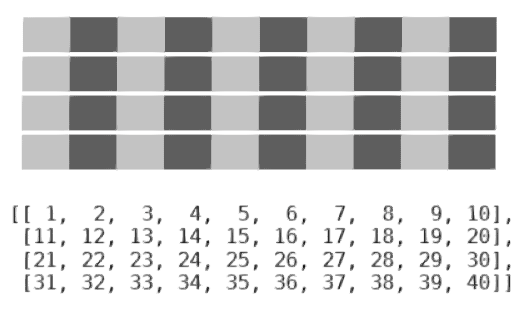
Slicing a 2-d array is similar to slicing a Pandas dataframe.
'''
The array, a_2, is structured into cells, rows, and cols.
'''
#access a cell
In[]: a_2[0][0]
Out[]: 1
In[]: a_2[2][4]
Out[]: 25
'''
There is an alternative syntax for accessing the same data.
It's a short of short-hand for index slicing because it uses
fewer brackets for the same effect.
'''
In[]: a_2[0,0]
Out[]: 1
In[]: a_2[2,4]
Out[]: 25
#access a row
In[]: a_2[0]
Out[]: array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
In[]: a_2[3]
Out[]: array([31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40])
#access multipul rows
In[]: a_2[2:4]
Out[]:
array([[21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
[31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40]])
#access a slice of a row
In[]: a_2[0][4:8]
Out[]: array([5, 6, 7, 8])
In[]: a_2[3][0:5]
Out[]: array([31, 32, 33, 34, 35])
#access a slice of multiple rows
In[]: a_2[0:3,[0,1]]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[11, 12],
[21, 22]])
In[]: a_2[0:3,[0,1,4]]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2, 5],
[11, 12, 15],
[21, 22, 25]])
#access a col
In[]: a_2[:,[1]]
Out[]:
array([[ 2],
[12],
[22],
[32]])
#access multiple cols
In[]: a_2[:,[1,9]]
Out[]:
array([[ 2, 10],
[12, 20],
[22, 30],
[32, 40]])
#access a slice of a col
In[]: a_2[1:3,[1]]
Out[]:
array([[12],
[22]])
#access a slice of multiple cols
In[]: a_2[1:3,[1,4]]
Out[]:
array([[12, 15],
[22, 25]])
#access even indexed rows ; beggining at index 0
In[]: a_2[::2,:]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30]])
#access even indexed cols
In[]: a_2[:,::2]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9],
[11, 13, 15, 17, 19],
[21, 23, 25, 27, 29],
[31, 33, 35, 37, 39]])
#apply a conditional to the array
In[]: a_2[a_2 > 23]
Out[]: array([24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40])
#apply a chained conditional to the array
In[]: a_2[(a_2 > 6) & (a_2 < 14)]
Out[]: array([ 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13])
#apply an operator bewteen two cols ; here adds col at index 1 to col at index 4
In[]: a_2[:,[1]] + a_2[:,[4]]
Out[]:
array([[ 7],
[27],
[47],
[67]])
#apply an operator bewteen two rows; here is the product of row at index 0 and index 3
In[]: a_2[0] * a_2[3]
Out[]: array([ 31, 64, 99, 136, 175, 216, 259, 304, 351, 400])
Slicing a 3d array:
Array slicing starts to get a little tricky when applied to arrays of 3 or more dimensions.
'''
'''
In[]: a_3 = np.arange(1, 41).reshape(4, 5, 2) ; print(a_3)
Out[]:
[[[ 1 2]
[ 3 4]
[ 5 6]
[ 7 8]
[ 9 10]]
[[11 12]
[13 14]
[15 16]
[17 18]
[19 20]]
[[21 22]
[23 24]
[25 26]
[27 28]
[29 30]]
[[31 32]
[33 34]
[35 36]
[37 38]
[39 40]]]
Visualized the shape of a_3 could look like this:
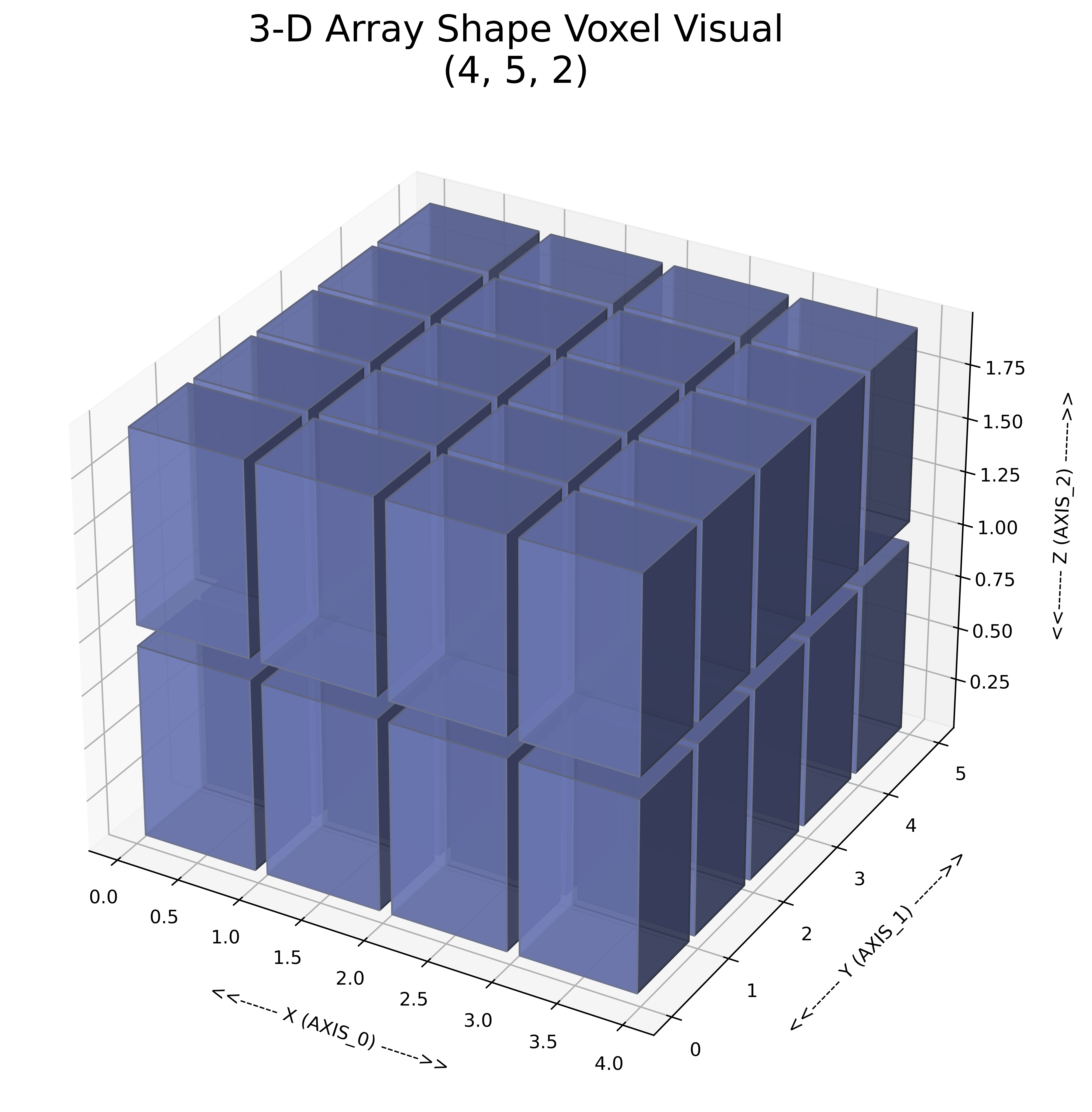
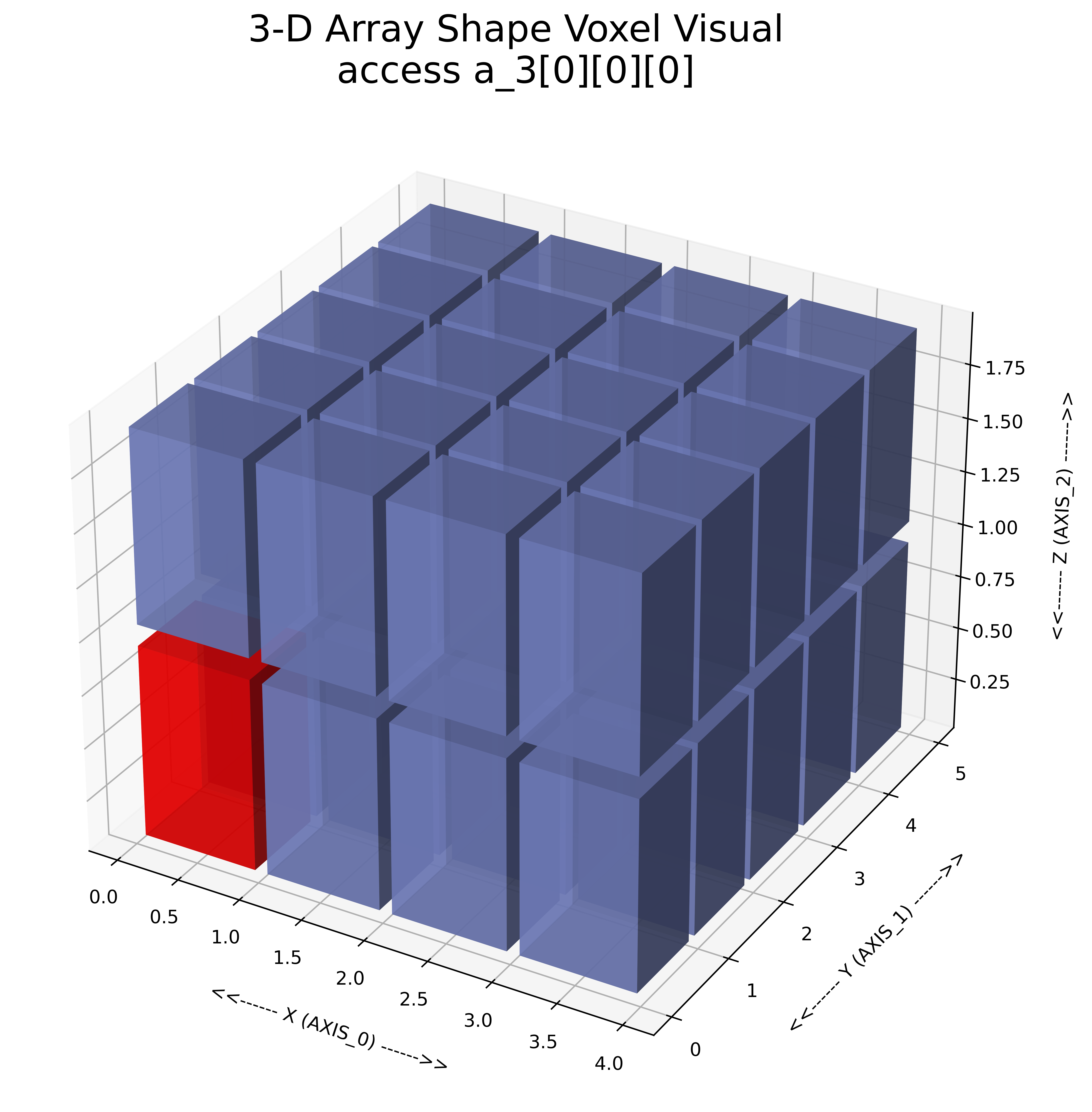
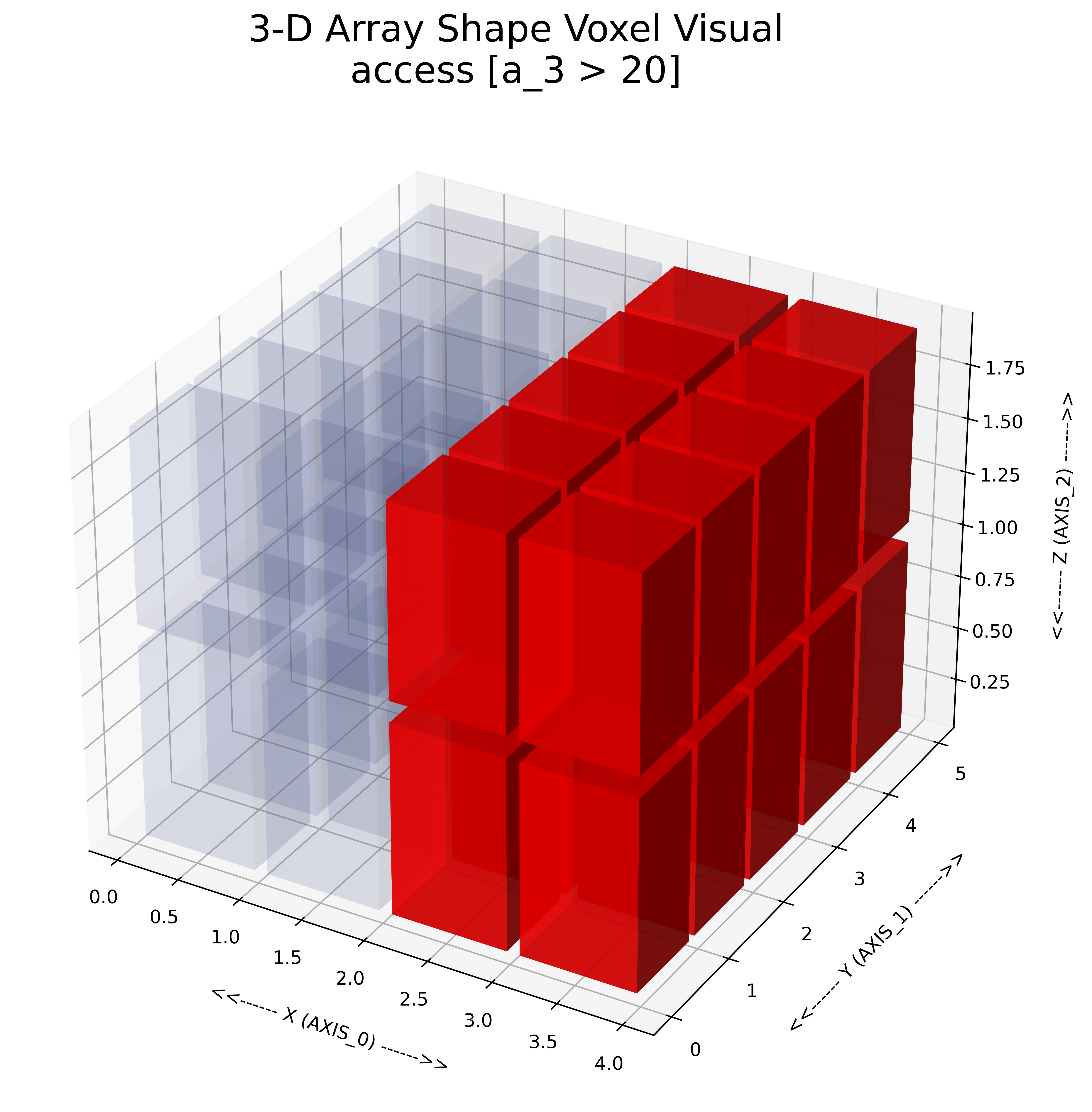
Each voxel represents a memory block where data exists. From here I'm going to highlight the blocks that correspond to the data we are accessing in red. This should make it a little easier to visualize what data we are accessing and how.
Access the first data point:
'''
Here we'll access the first data point in the 3-d array a_3.
Axis_0 [0] Axis_1 [0] and axis_2 [0]
'''
In[]: a_3[0][0][0]
Out[]: 1
#alternatively
In[]: a_3[0,0,0]
Out[]: 1
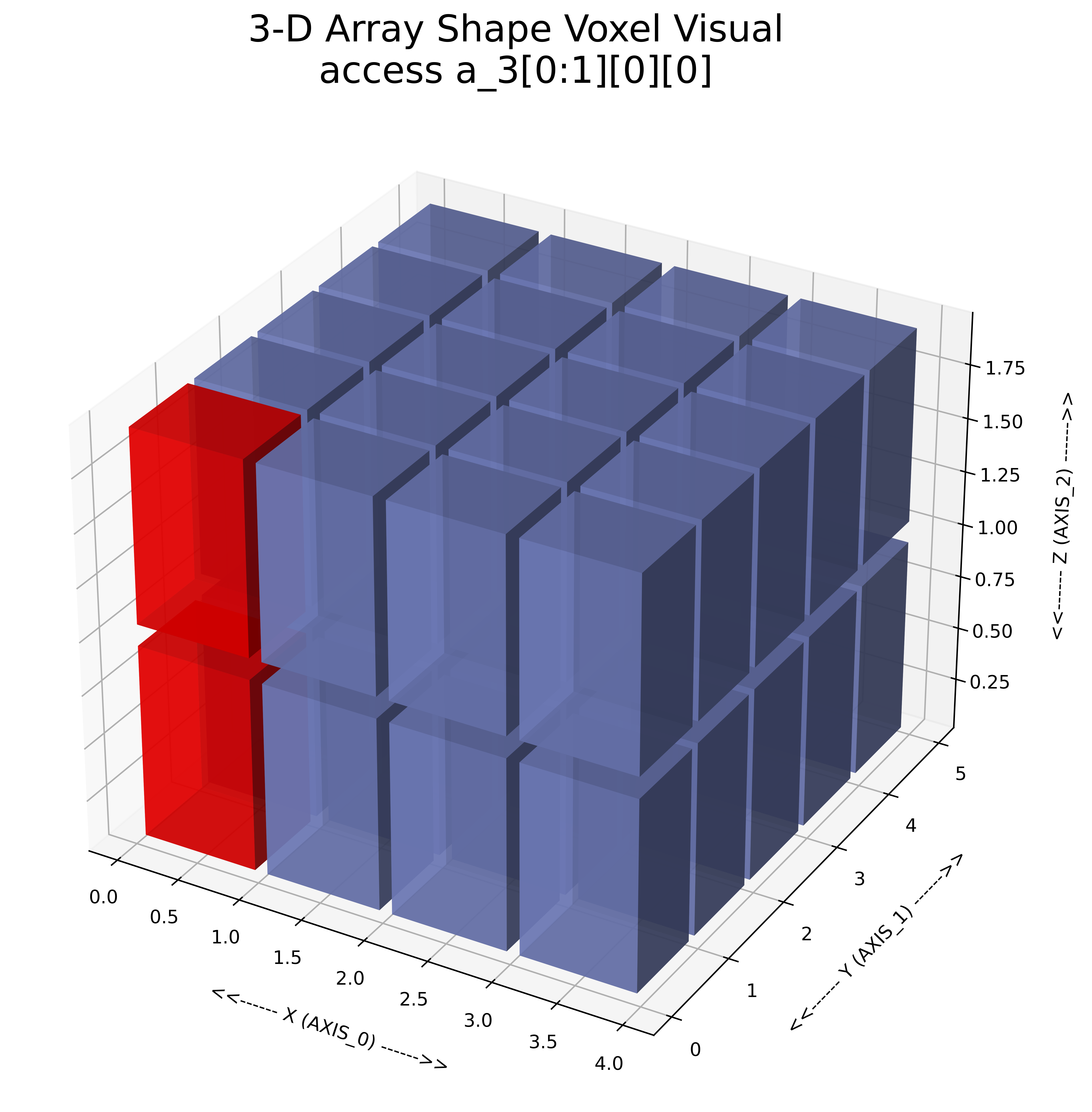
#Access axis_0
In[]: a_3[0:][0][0]
out[]: array([1, 2])
#alternatively
In[]: a_3[0,0,0:]
Out[]: array([1, 2])
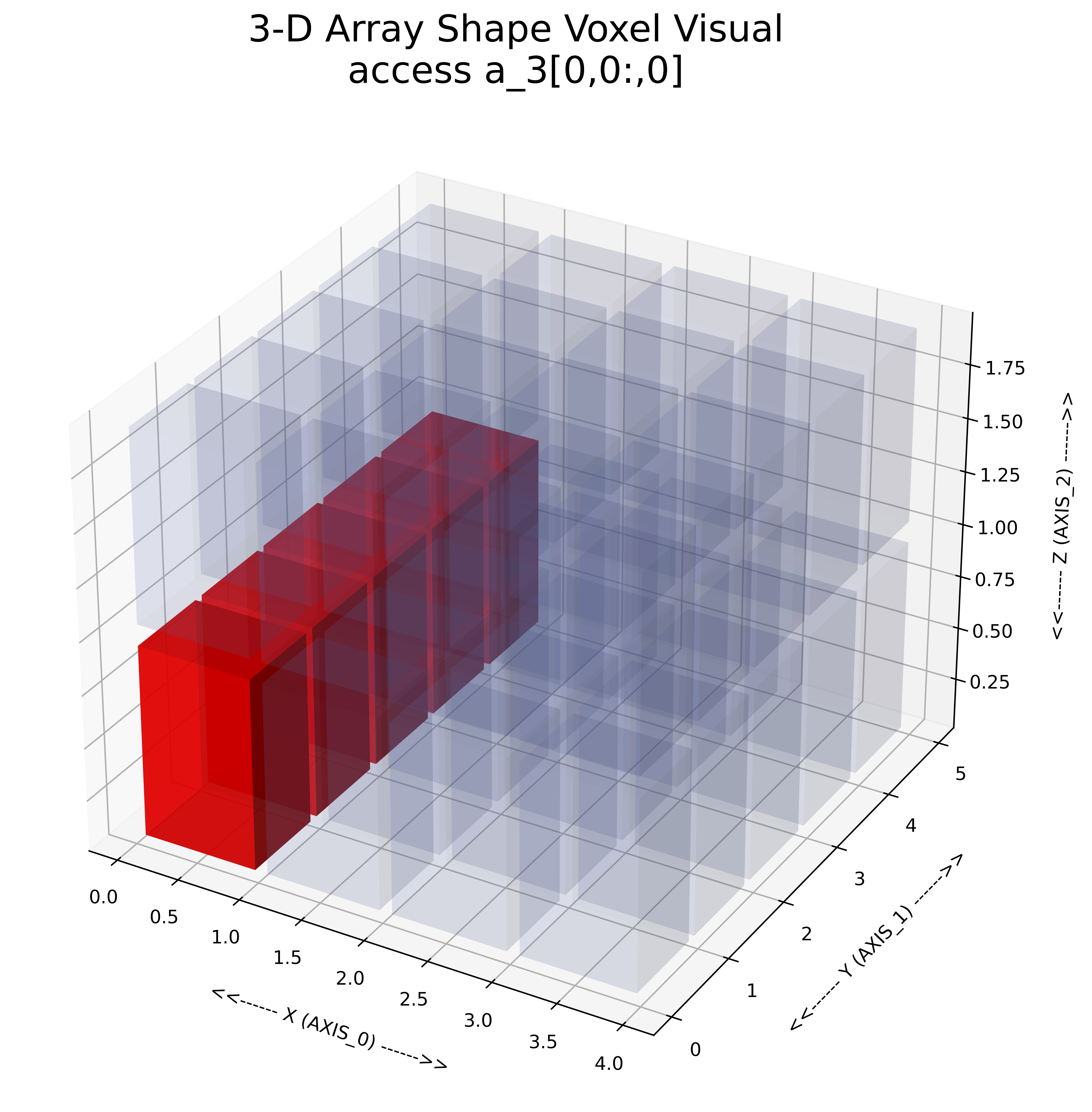
#access the axis_1
In[]: a_3[0,0:,0]
Out[]: array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
#access axis_0
In[]: a_3[0]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]])
#alternatively
In[]: a_3[0,0:,0:]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]])
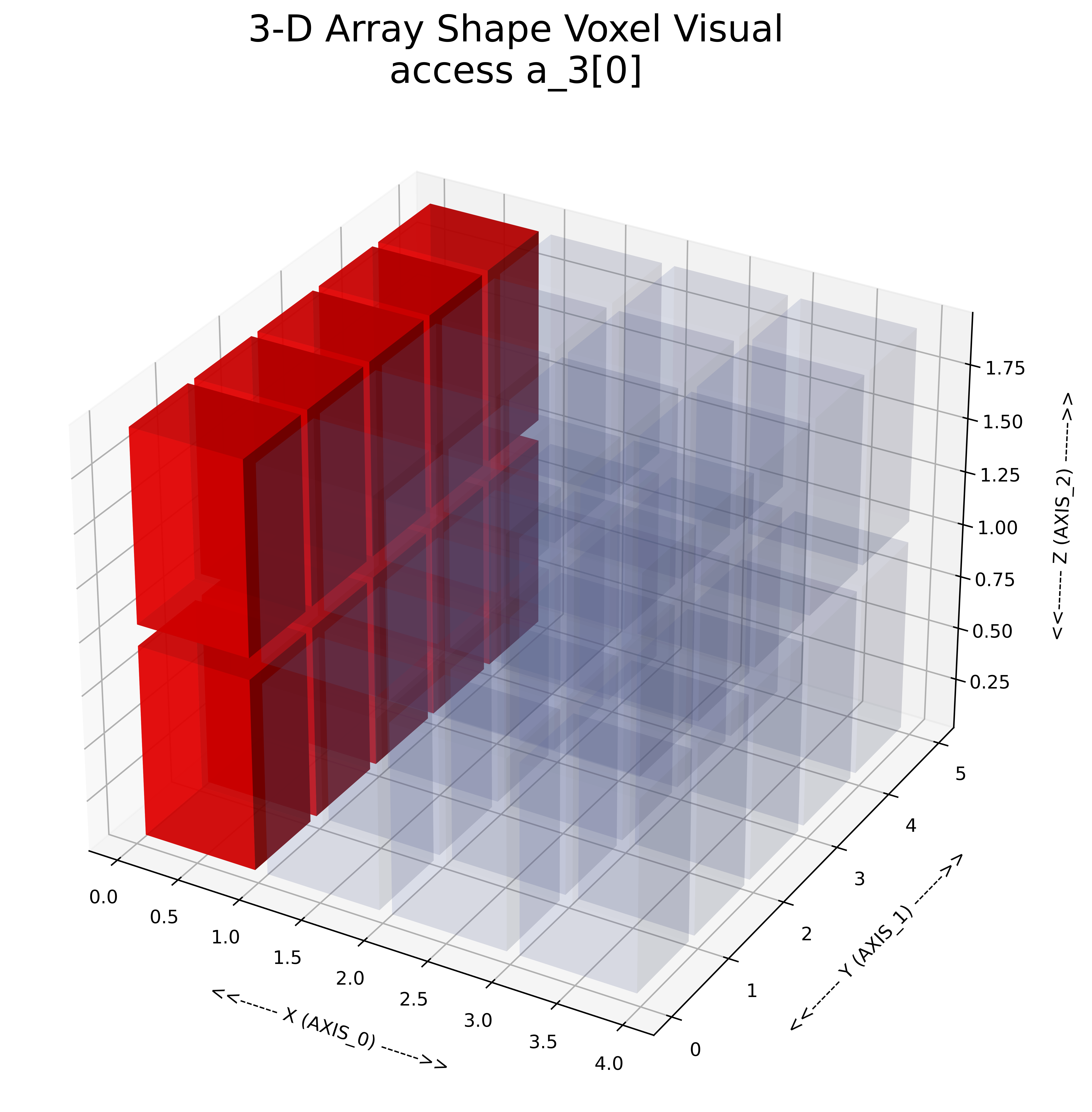
#
In[]: a_3[0:,0,0]
Out[]: array([ 1, 11, 21, 31])
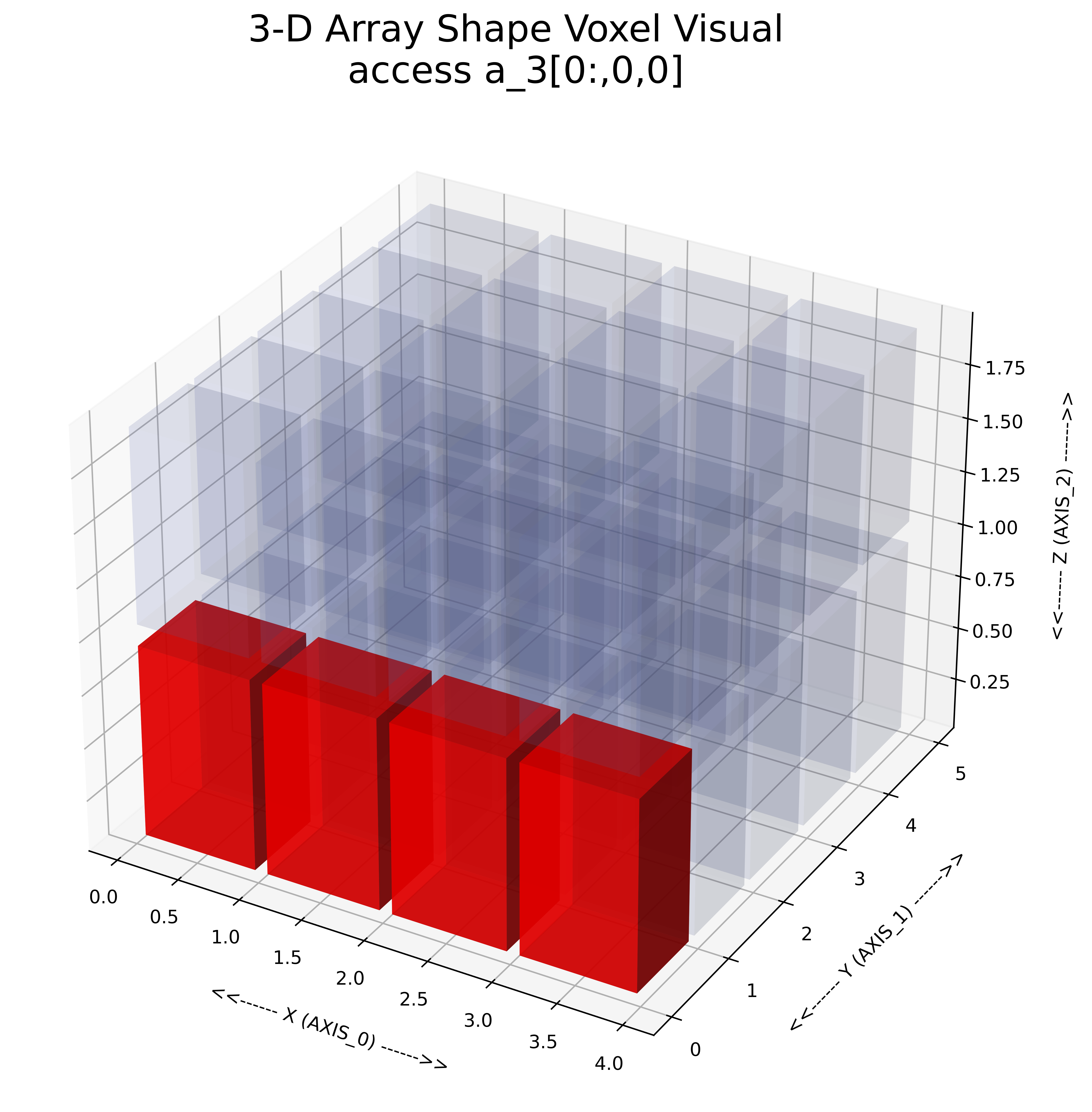
#
In[]: a_3[0:,0,0:]
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[11, 12],
[21, 22],
[31, 32]])
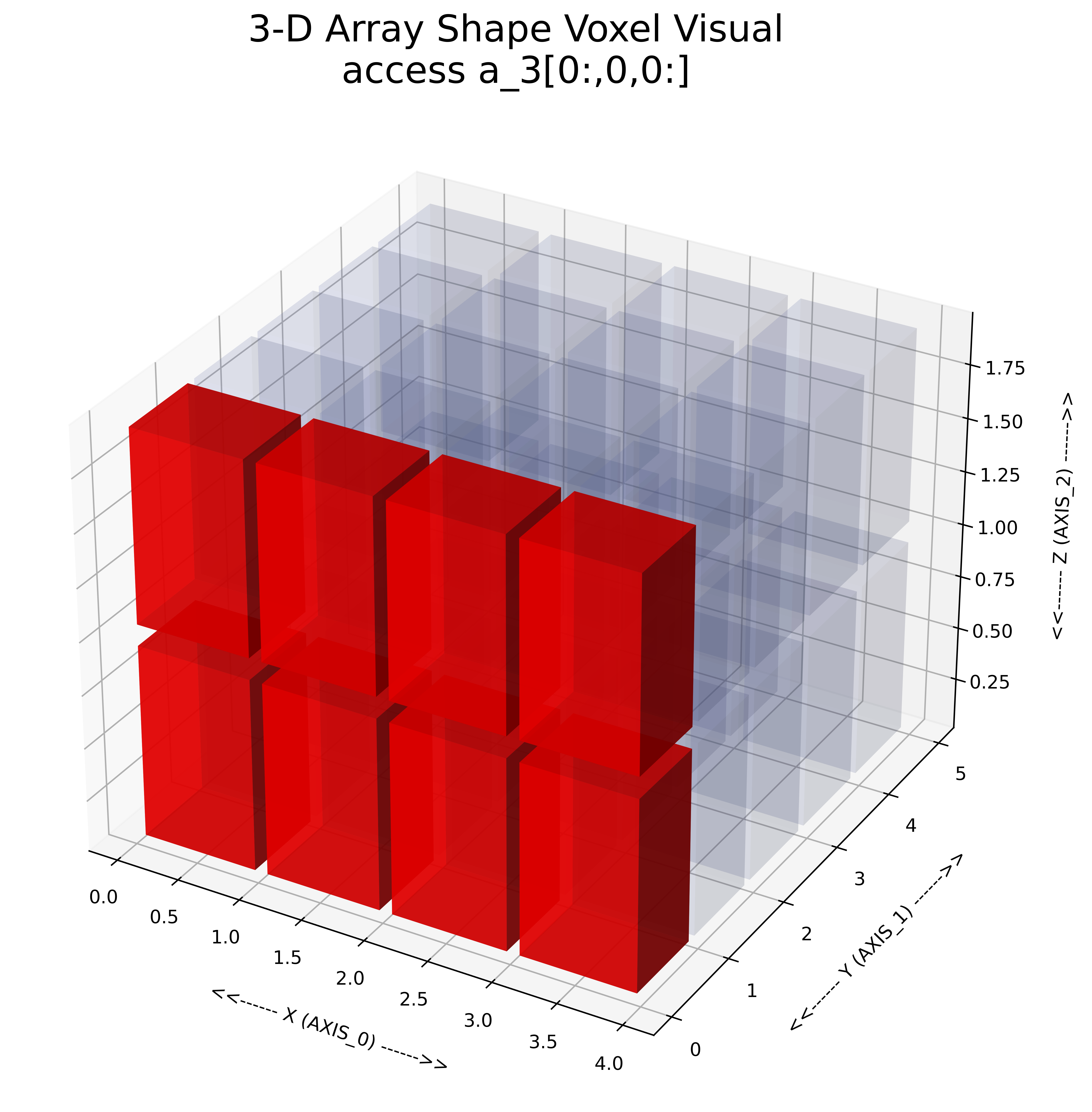
#
In[]: a_3[1,0:1,0]
Out[]: array([11])
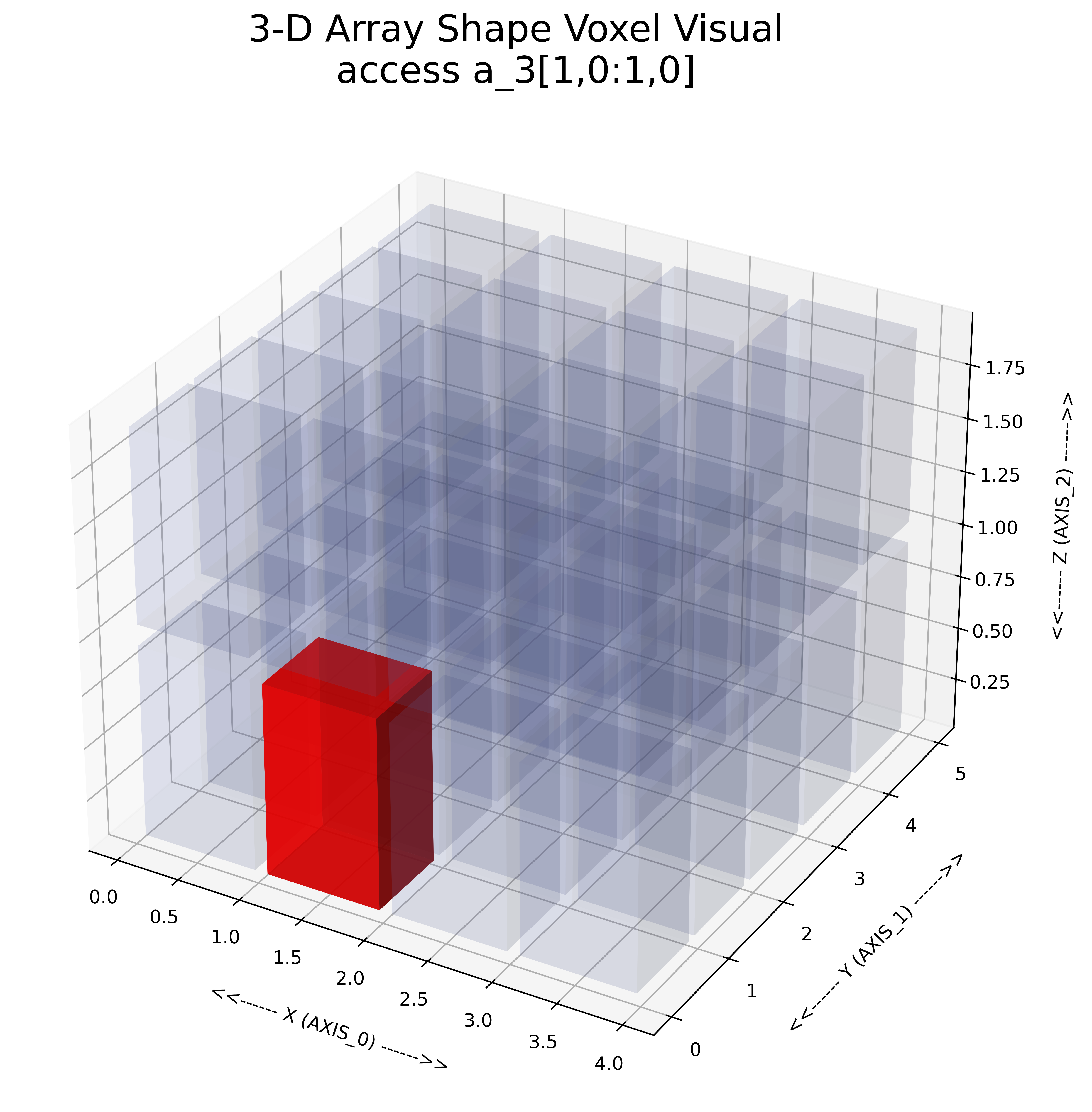
#
In[]: a_3[1,0,0:2]
Out[]: array([11, 12])
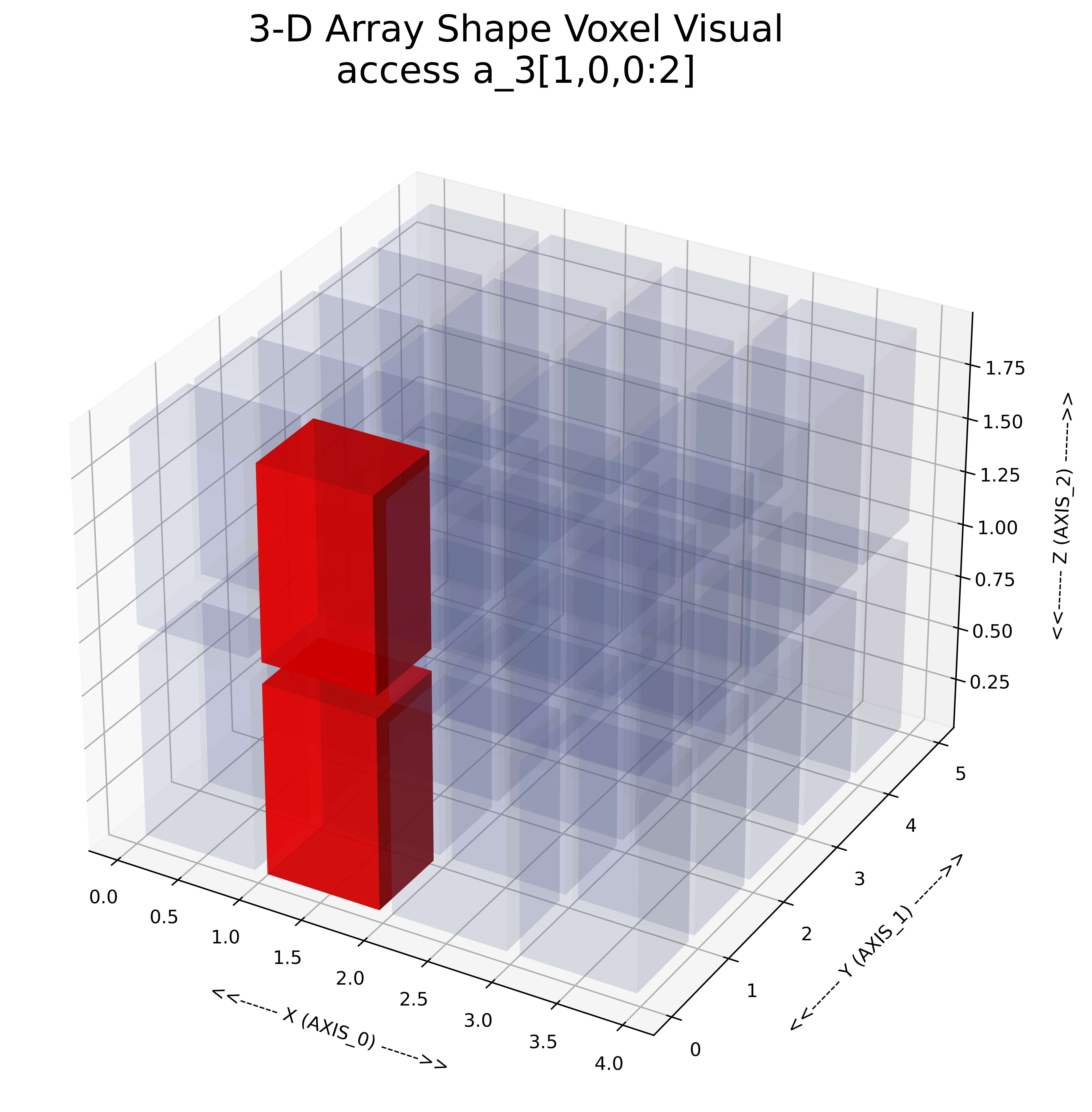
#
In[]: a_3[1,0:,0]
Out[]: array([11, 13, 15, 17, 19])
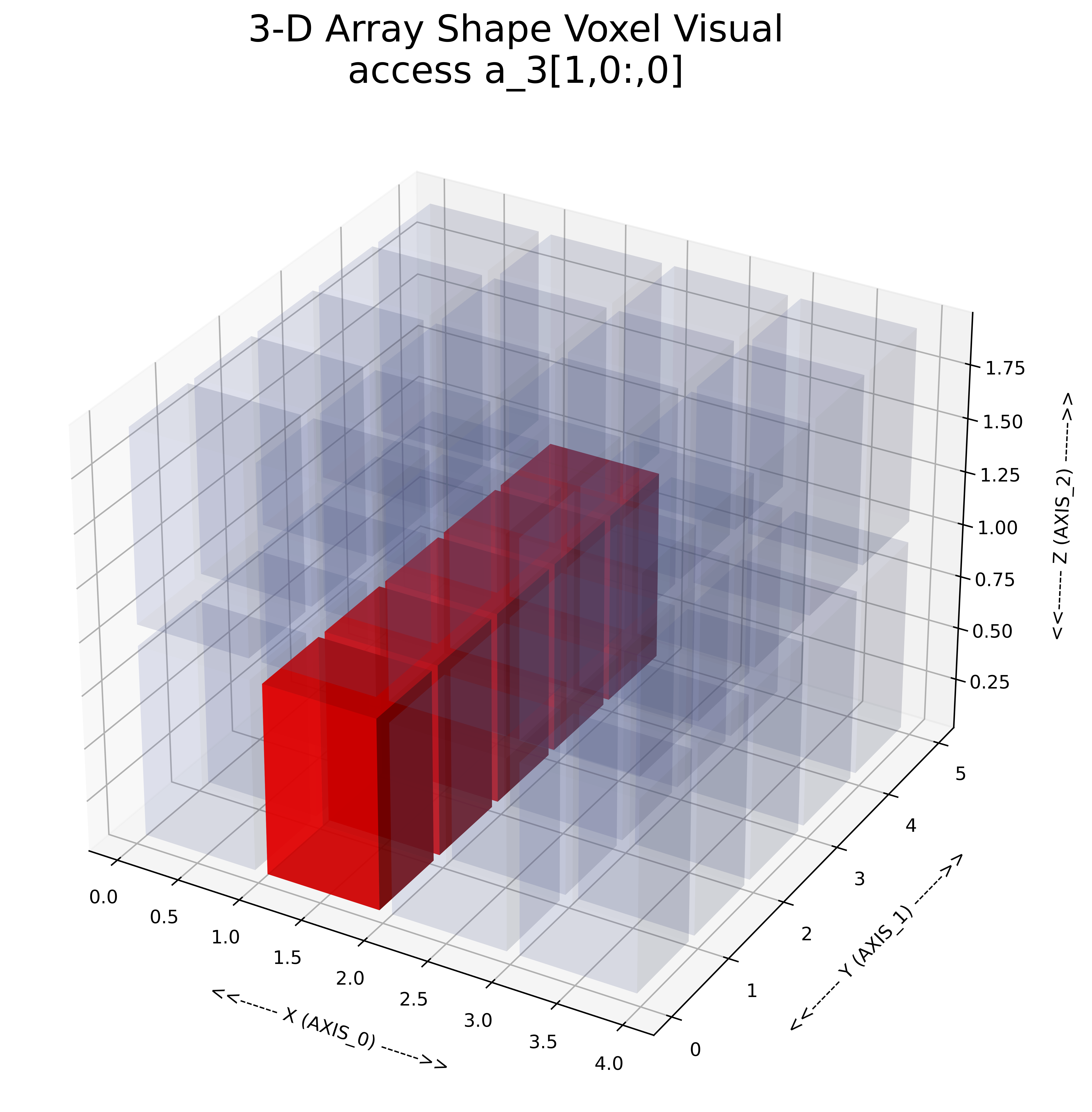
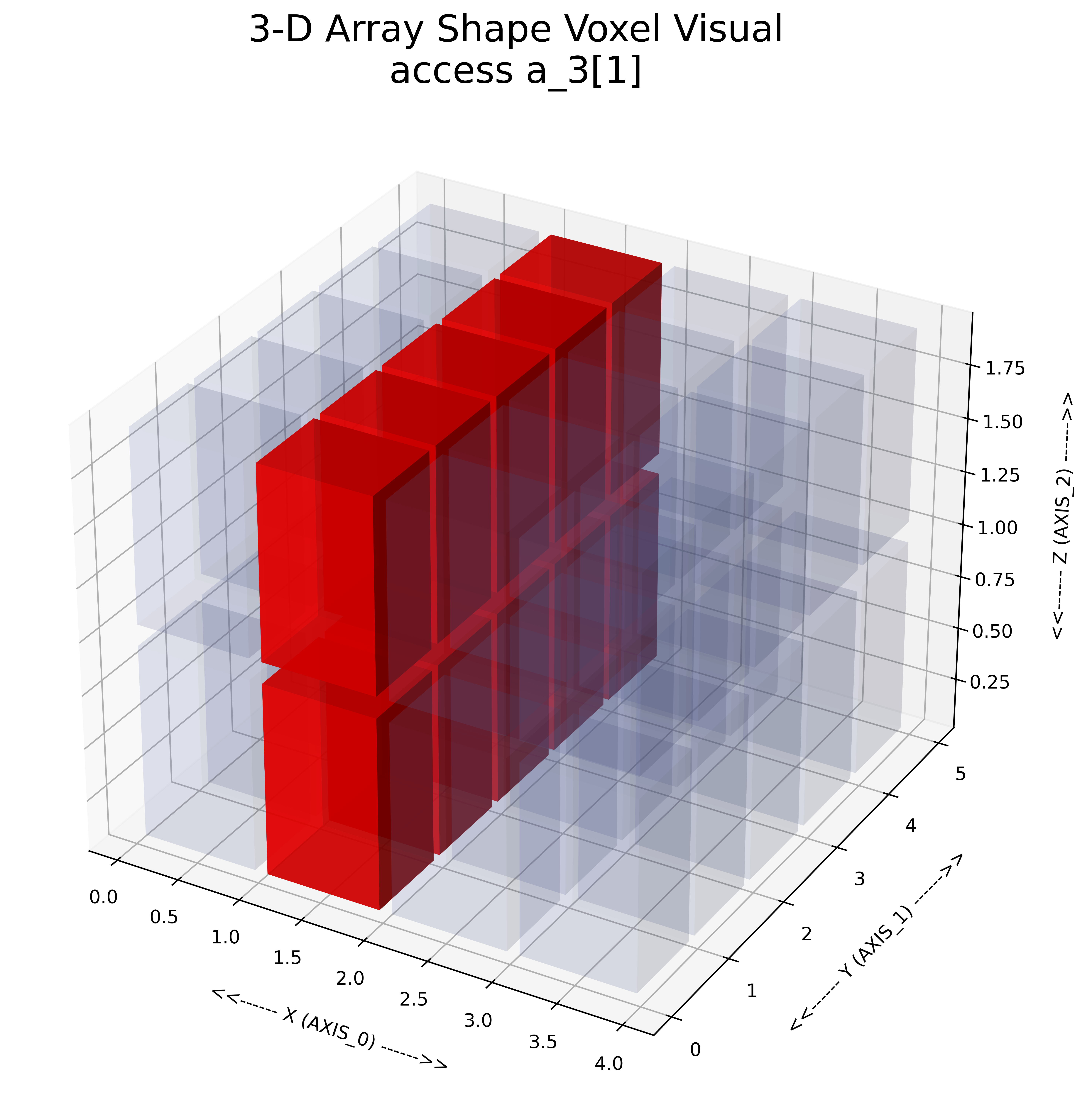
#
In[]: a_3[1]
Out[]:
array([[11, 12],
[13, 14],
[15, 16],
[17, 18],
[19, 20]])
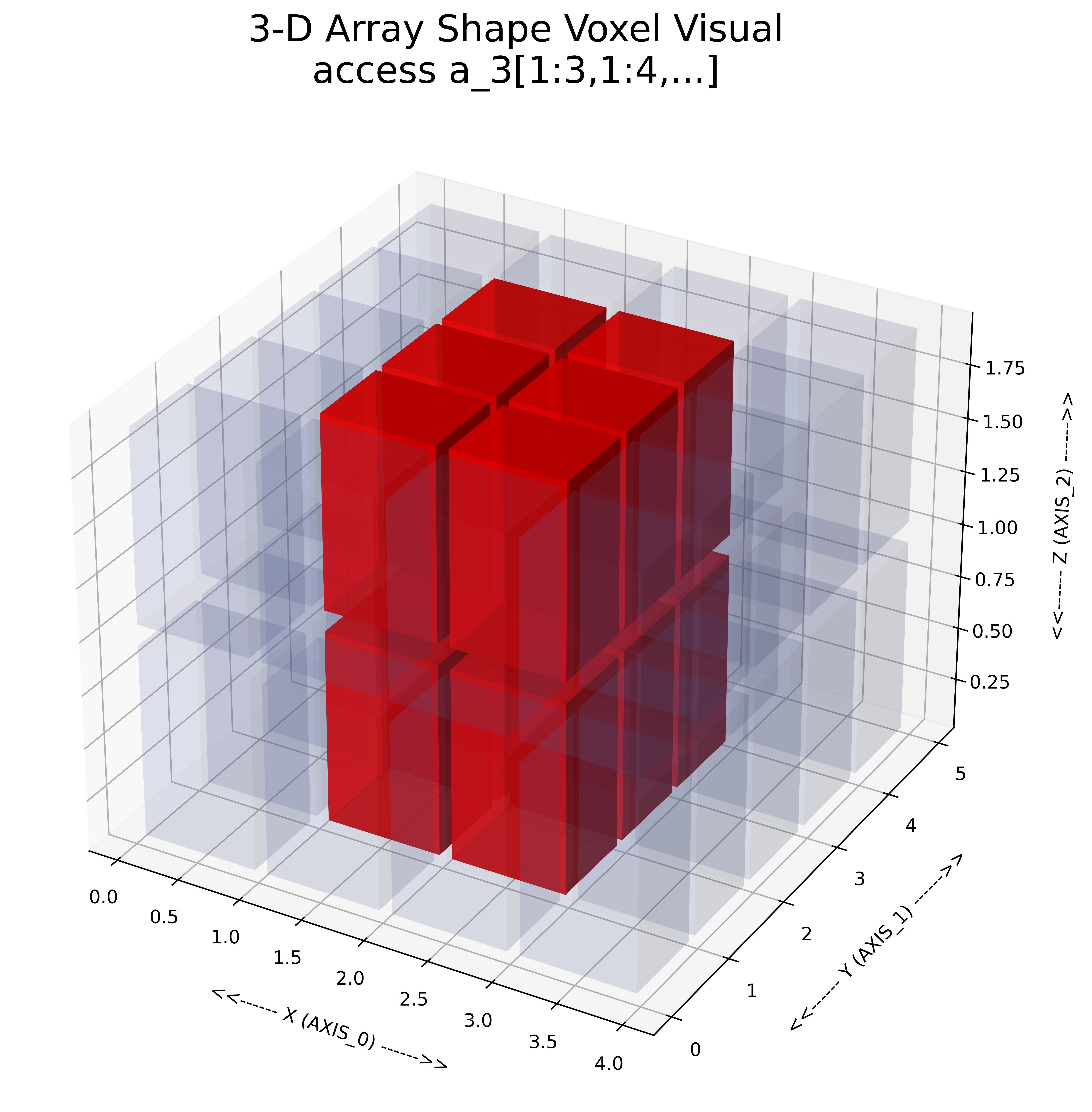
#
In[]: a_3[1:3,1:4,...]
Out[]:
array([[[13, 14],
[15, 16],
[17, 18]],
[[23, 24],
[25, 26],
[27, 28]]])
Apply operators to slice the data:
#access all data greater than 20
In[]: a_3[a_3 > 20]
Out[]: array([21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30,
31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40])
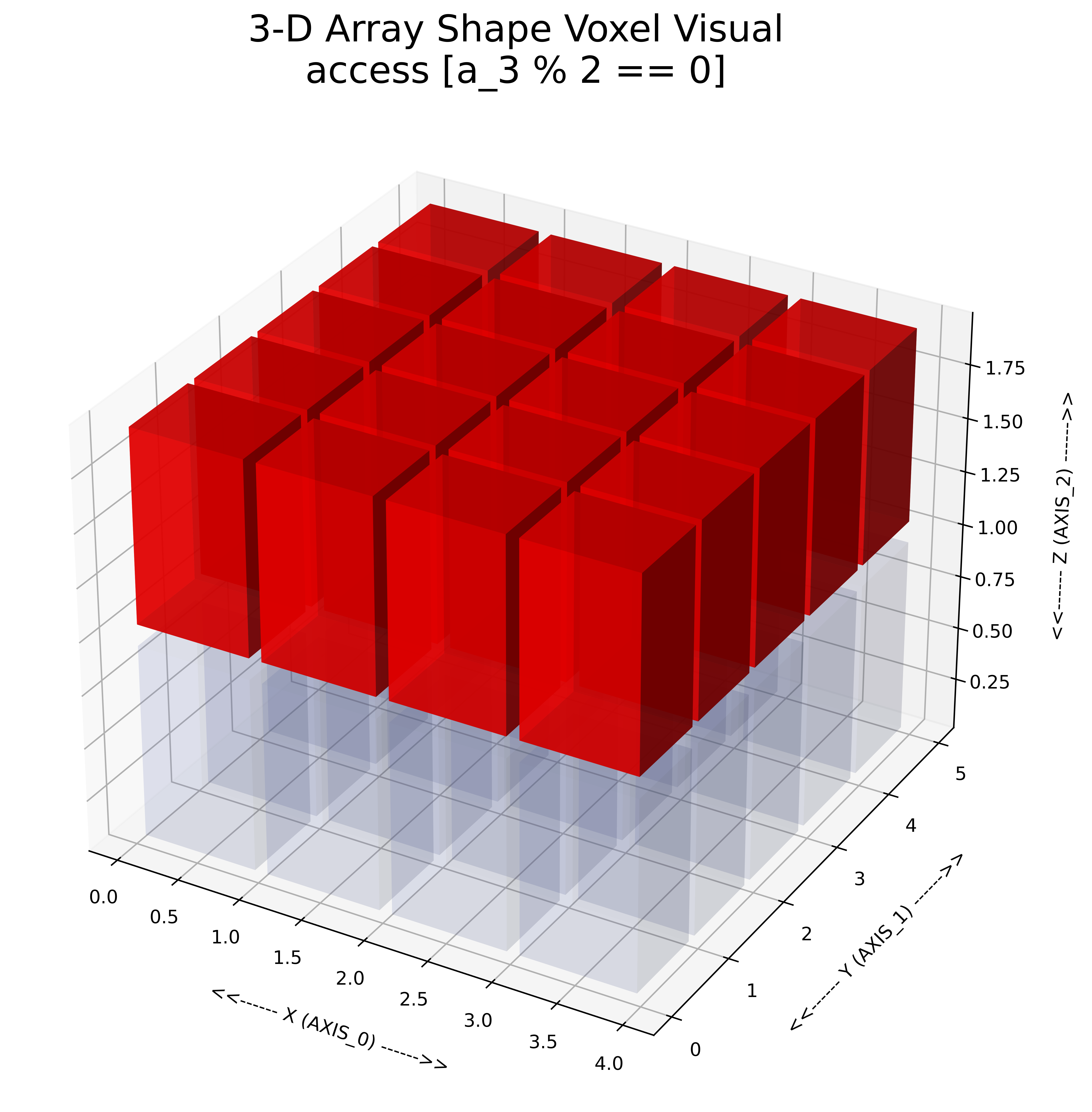
#all data that equally divides by 2
In[]: a_3[a_3 % 2 == 0]
Out[]: array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,
22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40])
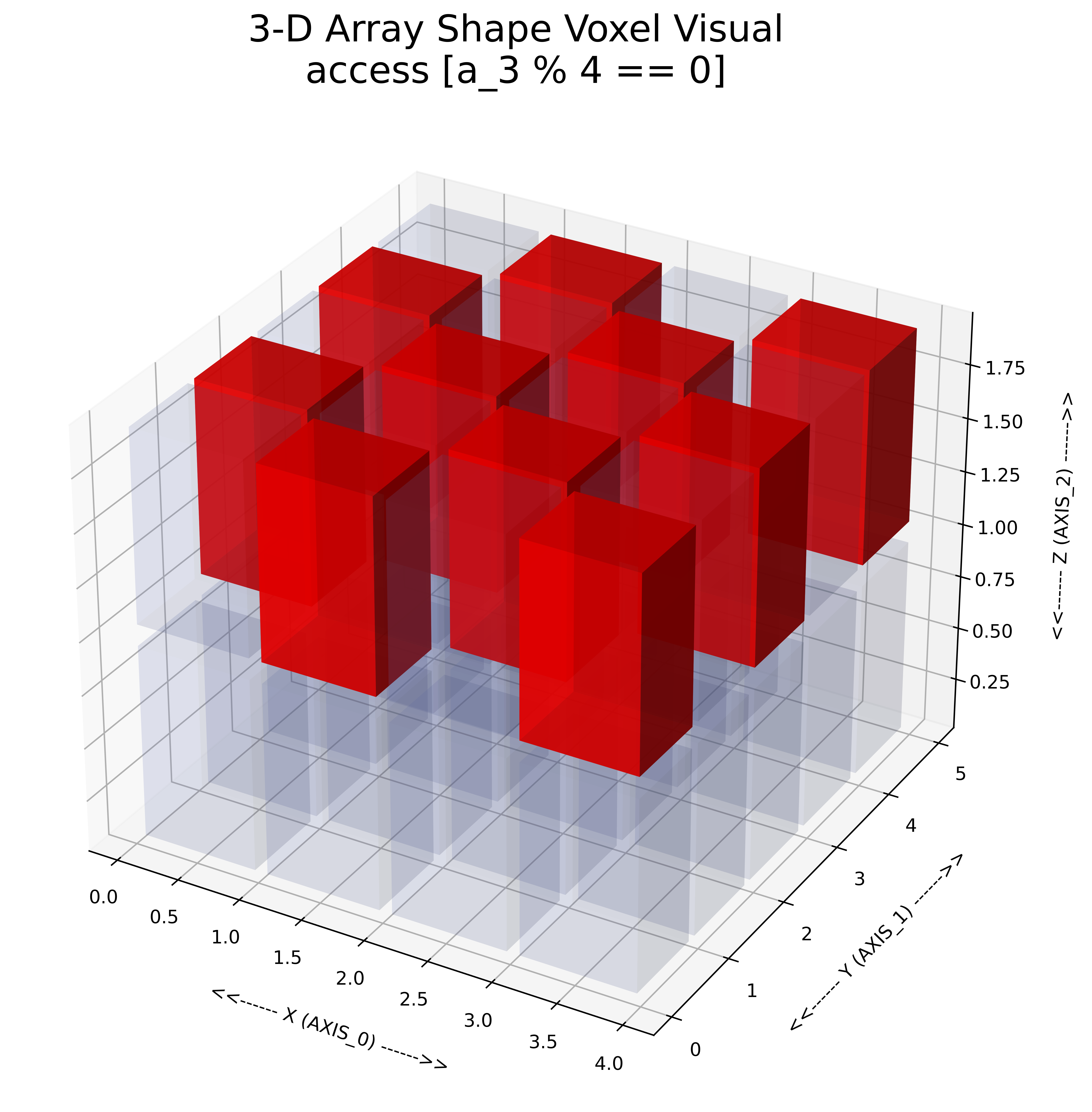
#all data that equally divides by 4
In[]: a_3[a_3 % 4 == 0]
Out[]: array([ 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40])
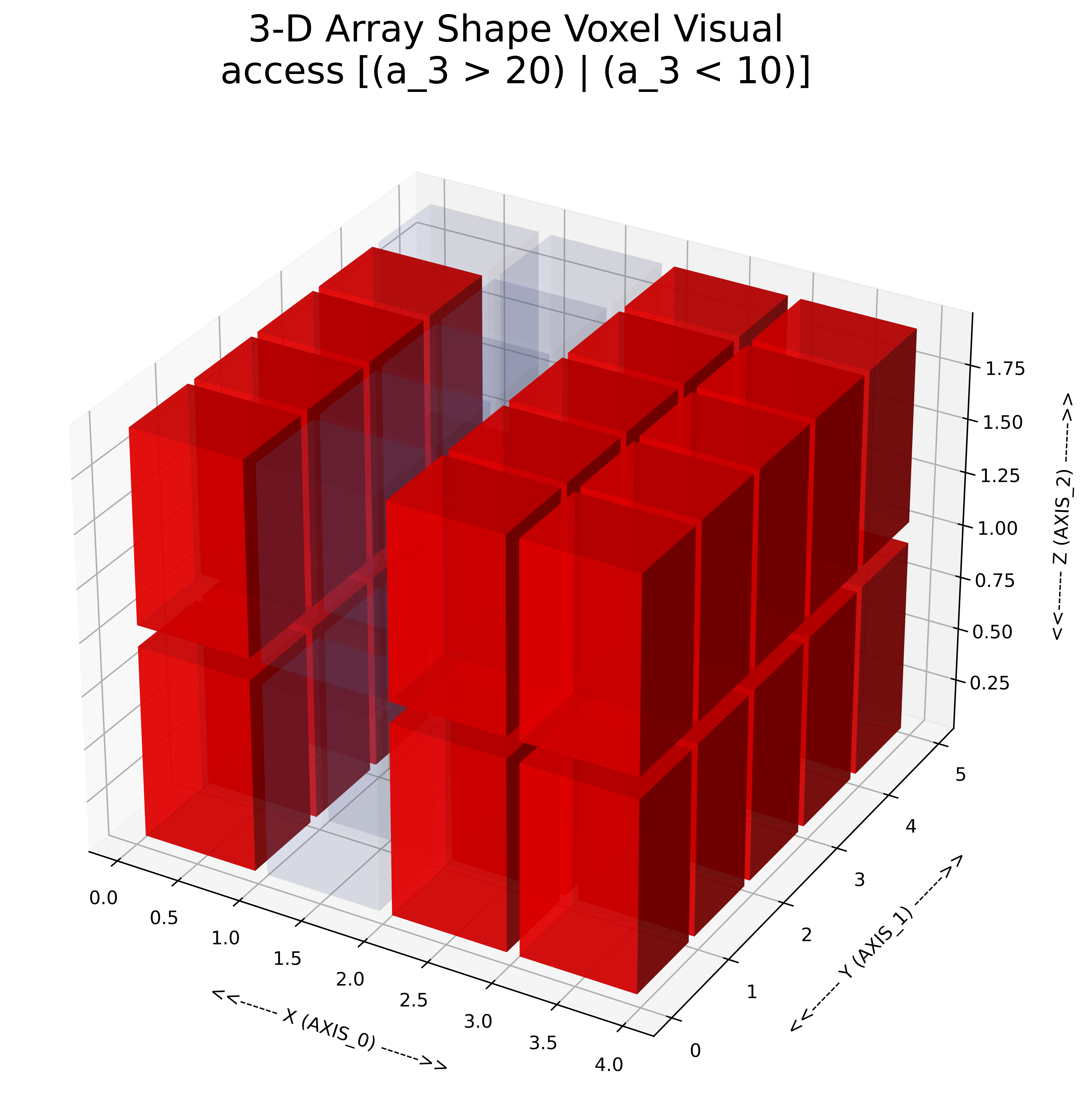
#all data greater than 20 or less than 10
In[]: a_3[(a_3 > 20) | (a_3 < 10)]
Out[]: array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 21,
22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31,
32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40])
#all data equally divisible by 3 and not equally divisible by 2
In[]: a_3[(a_3 % 3 == 0) & (a_3 % 2 != 0)]
Out[]: array([ 3, 9, 15, 21, 27, 33, 39])
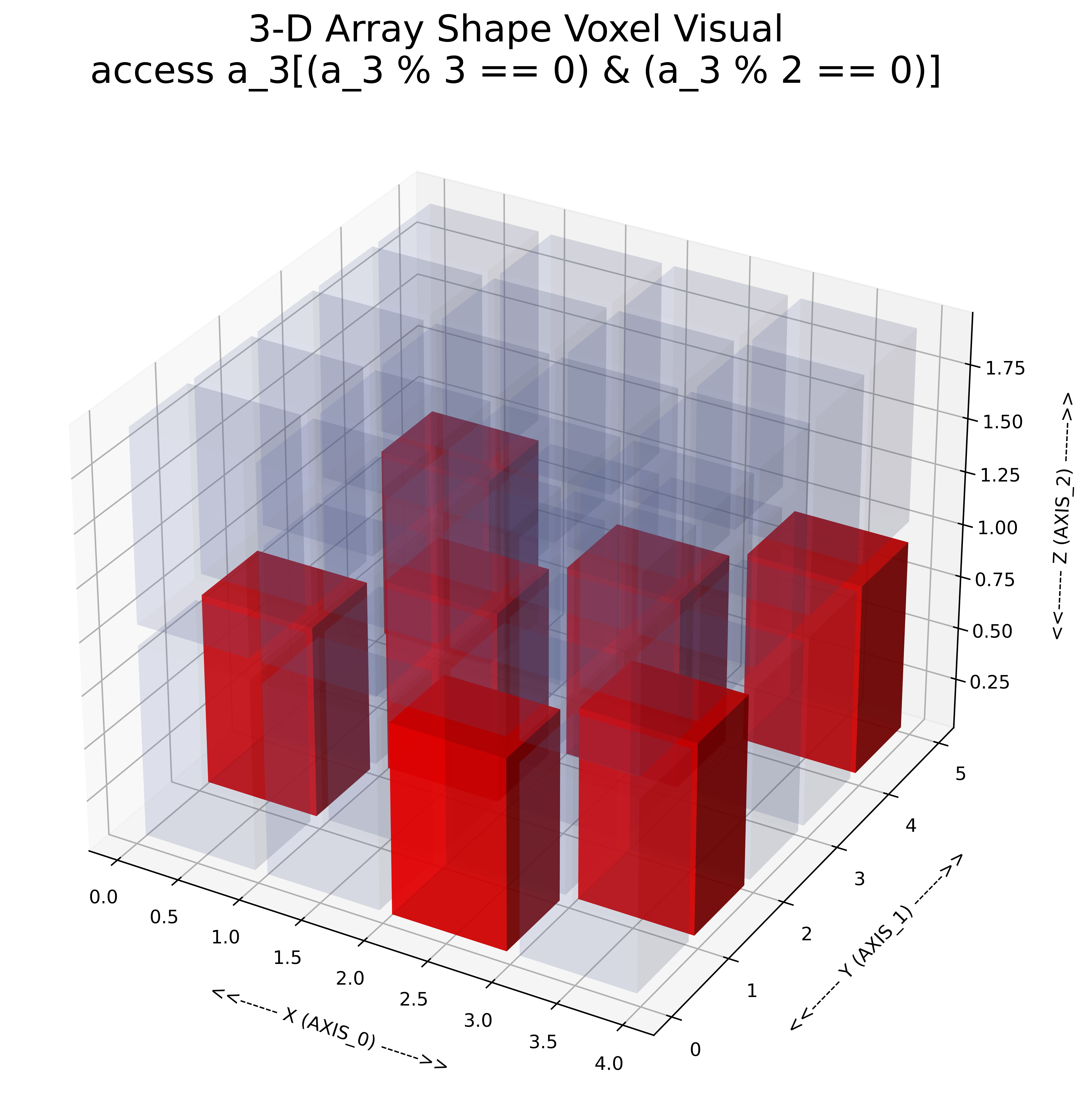
If anything I suggest exploring 3-d arrays—it can be a lot of fun.
Array Modification Methods
Modifying arrays with different methods can achieve certain things depending on what you are trying to accomplish.
Convert data type of an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33,
34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,
51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59])
#convert to floats
In[]: a_4.astype(float)
Out[]:
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12.,
13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25.,
26., 27., 28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34., 35., 36., 37., 38.,
39., 40., 41., 42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., 48., 49., 50., 51.,
52., 53., 54., 55., 56., 57., 58., 59.])
#convert to strings
In[]: a_4.astype(str)
Out[]:
array(['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '10', '11', '12',
'13', '14', '15', '16', '17', '18', '19', '20', '21', '22', '23',
'24', '25', '26', '27', '28', '29', '30', '31', '32', '33', '34',
'35', '36', '37', '38', '39', '40', '41', '42', '43', '44', '45',
'46', '47', '48', '49', '50', '51', '52', '53', '54', '55', '56',
'57', '58', '59'], dtype='<U11')
Transpose an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39]],
[[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59]]])
In[]: np.transpose(a_4)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 20, 40],
[ 5, 25, 45],
[10, 30, 50],
[15, 35, 55]],
[[ 1, 21, 41],
[ 6, 26, 46],
[11, 31, 51],
[16, 36, 56]],
[[ 2, 22, 42],
[ 7, 27, 47],
[12, 32, 52],
[17, 37, 57]],
[[ 3, 23, 43],
[ 8, 28, 48],
[13, 33, 53],
[18, 38, 58]],
[[ 4, 24, 44],
[ 9, 29, 49],
[14, 34, 54],
[19, 39, 59]]])
Return the inverse of an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33,
34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,
51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59])
In[]: np.flip(a_4)
Out[]:
array([59, 58, 57, 56, 55, 54, 53, 52, 51, 50, 49, 48, 47, 46, 45, 44, 43,
42, 41, 40, 39, 38, 37, 36, 35, 34, 33, 32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26,
25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9,
8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0])
#also flip on a specific axis
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39]],
[[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59]]])
In[]: np.flip(a_4, axis=2)
Out[]:
array([[[ 4, 3, 2, 1, 0],
[ 9, 8, 7, 6, 5],
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10],
[19, 18, 17, 16, 15]],
[[24, 23, 22, 21, 20],
[29, 28, 27, 26, 25],
[34, 33, 32, 31, 30],
[39, 38, 37, 36, 35]],
[[44, 43, 42, 41, 40],
[49, 48, 47, 46, 45],
[54, 53, 52, 51, 50],
[59, 58, 57, 56, 55]]])
Rotate data in an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: np.roll(a_4, shift=1, axis=None)
Out[]:
array([[[59, 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 15, 16, 17, 18]],
[[19, 20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27, 28],
[29, 30, 31, 32, 33],
[34, 35, 36, 37, 38]],
[[39, 40, 41, 42, 43],
[44, 45, 46, 47, 48],
[49, 50, 51, 52, 53],
[54, 55, 56, 57, 58]]])
Flatten an array with ravel and flatten:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39]],
[[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59]]])
In[]: np.ravel(a_4, order="C")
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33,
34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,
51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59])
Move axes of an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39]],
[[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59]]])
In[]: np.moveaxis(a_4, -1, 0)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 5, 10, 15],
[20, 25, 30, 35],
[40, 45, 50, 55]],
[[ 1, 6, 11, 16],
[21, 26, 31, 36],
[41, 46, 51, 56]],
[[ 2, 7, 12, 17],
[22, 27, 32, 37],
[42, 47, 52, 57]],
[[ 3, 8, 13, 18],
[23, 28, 33, 38],
[43, 48, 53, 58]],
[[ 4, 9, 14, 19],
[24, 29, 34, 39],
[44, 49, 54, 59]]])
Switch 2 axes in an array:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0, 60).reshape(3,4,5)
In[]: a_4
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39]],
[[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49],
[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59]]])
In[]: np.swapaxes(a_4, axis1=0, axis2=2)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 20, 40],
[ 5, 25, 45],
[10, 30, 50],
[15, 35, 55]],
[[ 1, 21, 41],
[ 6, 26, 46],
[11, 31, 51],
[16, 36, 56]],
[[ 2, 22, 42],
[ 7, 27, 47],
[12, 32, 52],
[17, 37, 57]],
[[ 3, 23, 43],
[ 8, 28, 48],
[13, 33, 53],
[18, 38, 58]],
[[ 4, 24, 44],
[ 9, 29, 49],
[14, 34, 54],
[19, 39, 59]]])
Convert an array to at least 1, 2, or 3 dimensions:
#
In[]: a_7 = np.arange(0, 5)
In[]: a_7
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
In[]: np.atleast_2d(a_7)
Out[]: array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]])
In[]: np.atleast_3d(a_7)
Out[]:
array([[[0],
[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]]])
Return a boolean value for an arrays n-dimensional truth:
#
In[]: a_7 = np.arange(0, 5)
In[]: a_7
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
In[]: np.atleast_3d(a_7) is a_7
Out[]: False
In[]: np.atleast_2d(a_7) is a_7
Out[]: False
In[]: np.atleast_1d(a_7) is a_7
Out[]: True
Check an array for np.nan and np.inf (Infinite) values:
#
In[]: a_8 = np.array([0, 1, np.nan, 2, 3, 4])
In[]: np.asarray_chkfinite(a_8)
Out[]:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-69-98f638cde909>", line 1, in <module>
np.asarray_chkfinite(a_8)
File "C:\Users\antho\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\numpy\lib\function_base.py", line 488, in asarray_chkfinite
raise ValueError(
ValueError: array must not contain infs or NaNs
In[]: a_7 = np.arange(0, 5)
In[]: np.asarray_chkfinite(a_7)
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
Join multiple arrays along an existing axis with np.concatenate:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]]])
In[]: a_2 = np.array([[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]])
In[]: np.concatenate([a_2, a_3])
Out[]:
array([[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
Join multiple arrays on a new axis with np.stack:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]]])
In[]: a_6 = np.zeros((4, 5))
In[]: np.stack([a_3, a_6], axis=0)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[10., 11., 12., 13., 14.],
[20., 21., 22., 23., 24.]],
[[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]])
In[]: np.stack([a_3, a_6], axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[10., 11., 12., 13., 14.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[20., 21., 22., 23., 24.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]])
In[]: np.stack([a_3, a_6], axis=2)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0., 0.],
[ 1., 0.],
[ 2., 0.],
[ 3., 0.],
[ 4., 0.]],
[[ 5., 0.],
[ 6., 0.],
[ 7., 0.],
[ 8., 0.],
[ 9., 0.]],
[[10., 0.],
[11., 0.],
[12., 0.],
[13., 0.],
[14., 0.]],
[[20., 0.],
[21., 0.],
[22., 0.],
[23., 0.],
[24., 0.]]])
Vertically stack arrays of the same size with np.vstack:
#
In[]: a_1 = np.arange(0, 20) ; a_2 = np.arange(20, 30) #to vstack these arrays they must be the same size
#change the arrays by assigning sections to new obj arrays
In[]: a_1_1 = a_1[0:10] #size = 10
In[]: a_1_2 = a_1[10:20] #size = 10
In[]: a_3 = np.vstack((a_1_1, a_2))
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29]])
In[]: a_3 = np.vstack((a_1_1, a_1_2, a_2))
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29]])
Horizontally stack arrays of different sizes:
#may be different sizes in a horizontal stack
In[]: a_1 = np.arange(0, 20) ; a_2 = np.arange(20, 30)
In[]: np.hstack((a_1, a_2))
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29])
Stack two or more 1-d arrays as columns with np.column_stack:
#
In[]: a_5 = np.arange(1,50,5) ; a_6 = np.arange(0,10)
In[]: np.column_stack((a_5, a_6))
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 0],
[ 6, 1],
[11, 2],
[16, 3],
[21, 4],
[26, 5],
[31, 6],
[36, 7],
[41, 8],
[46, 9]])
Stack two or more arrays vertically by rows with np.row_stack:
'''
Mostly for arrays of 3dim like; like pixel-data where (height, width, r_g_b_color)
'''
In[]: a_7 = np.array([5, 7, 9])
In[]: a_8 = np.array([2, 8, 10])
In[]: np.row_stack((a_8, a_7))
Out[]:
array([[ 2, 8, 10],
[ 5, 7, 9]])
In[]: a_9 = np.array([[5], [3], [8]])
In[]: a_10 = np.array([[3], [89], [55]])
In[]: np.row_stack((a_9, a_10))
Out[]:
array([[ 5],
[ 3],
[ 8],
[ 3],
[89],
[55]])
Split a 1-d array into sub arrays:
#
In[]: a_11 = np.arange(0,20)
In[]: a_11
Out[]:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19])
In[]: np.split(a_11, 4)
Out[]:
[array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]),
array([5, 6, 7, 8, 9]),
array([10, 11, 12, 13, 14]),
array([15, 16, 17, 18, 19])]
In[]: np.split(a_11, 5)
Out[]:
[array([0, 1, 2, 3]),
array([4, 5, 6, 7]),
array([ 8, 9, 10, 11]),
array([12, 13, 14, 15]),
array([16, 17, 18, 19])]
In[]: [(1, 20), (2, 10), (4, 5)]
Out[]:
[array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]),
array([10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19])]
Vertically split a 2-d array (must be evenly divisible):
#
In[]: a_13 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.vsplit(a_13, 5)
Out[]:
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]),
array([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]),
array([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]),
array([[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]]),
array([[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])]
Horizontally split an array:
#
In[]: a_12 = array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12],
[13, 14, 15, 16],
[17, 18, 19, 20]])
In[]: np.hsplit(a_12, 2)
Out[]:
[array([[ 1, 2],
[ 5, 6],
[ 9, 10],
[13, 14],
[17, 18]]),
array([[ 3, 4],
[ 7, 8],
[11, 12],
[15, 16],
[19, 20]])]
Construct an array with a tiled array:
#
In[]:np.tile(1, [2,2,2])
Out[]:
array([[[1, 1],
[1, 1]],
[[1, 1],
[1, 1]]])
In[]: np.tile(1, [1, 10, 5])
Out[]: array([[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]])
In[]: np.tile(0, [1, 5, 5])
Out[]: array([[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]])
In[]: np.tile(np.arange(0,3), [1, 5, 5])
Out[]:
array([[[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2],
[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2]]])
Construct an array with repeated items:
#
In[]: np.repeat(0, 10)
Out[]: array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
In[]: a_14 = np.arange(0, 4).reshape(2,2)
In[]: a_14
Out[]:
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
In[]: np.repeat(a_14, 5, axis=0)
Out[]: array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3])
In[]: np.repeat(a_14, 5, axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]])
In[]: np.repeat(a_14, [1,2], axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[0, 1, 1],
[2, 3, 3]])
Remove rows and or columns in a 2-d array with np.delete:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.delete(a_3, 1, 0)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.delete(a_3, [0,3], 1)
Out[]:
array([[ 1, 2, 4],
[ 6, 7, 9],
[11, 12, 14],
[21, 22, 24]])
Remove rows and or columns in a 3-d array with np.delete:
#
In[]: a_15 = array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: np.delete(a_15, 1, 0)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: np.delete(a_15, [1,2], 1) #axis specified as 1 for rows
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: np.delete(a_15, [0,3], 2) #change the axis to 2 for cols
Out[]: array([[[ 1, 2, 4],
[ 6, 7, 9],
[11, 12, 14],
[16, 17, 19],
[21, 22, 24]],
[[26, 27, 29],
[31, 32, 34],
[36, 37, 39],
[41, 42, 44],
[46, 47, 49]],
[[51, 52, 54],
[56, 57, 59],
[61, 62, 64],
[66, 67, 69],
[71, 72, 74]]])
Insert data into a 1-d array with np.insert:
#
In[]: a_4 = np.arange(0,10)
In[]: a_4
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In[]: np.insert(a_4, 10, 10)
Out[]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
In[]: np.insert(a_4, [5], 10)
Out[]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
#also insert another flat array
In[]: a_16 = np.arange(10, 30, 3)
In[]: a_16
Out[]: array([10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28])
In[]: np.insert(a_4, 10, a_16)
Out[]: array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28])
Insert data into a 2-d array with np.insert:
#
In[]: a_17 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.insert(a_17, 2, [69], axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 69, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 69, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 69, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 69, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 69, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.insert(a_17, 2, [69], axis=0)
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[69, 69, 69, 69, 69],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
Insert data into a 3-d array with np.insert:
#
In[]: a_15 = array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: np.insert(a_15, 2, [69], axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[69, 69, 69, 69, 69],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[69, 69, 69, 69, 69],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[69, 69, 69, 69, 69],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: np.insert(a_15, 2, [69], axis=2)
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 69, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 69, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 69, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 69, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 69, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 69, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 69, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 69, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 69, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 69, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 69, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 69, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 69, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 69, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 69, 72, 73, 74]]])
Insert new ndim based off other ndim:
#
In[]: a_15 = array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
In[]: a_15_2 = a_15[0] + 600 #create a new dim to insert
In[]: a_15_2
Out[]:
array([[600, 601, 602, 603, 604],
[605, 606, 607, 608, 609],
[610, 611, 612, 613, 614],
[615, 616, 617, 618, 619],
[620, 621, 622, 623, 624]])
In[]: np.insert(a_15, 2, a_15_2, axis=0) #insert that the newly created dim
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[ 15, 16, 17, 18, 19],
[ 20, 21, 22, 23, 24]],
[[ 25, 26, 27, 28, 29],
[ 30, 31, 32, 33, 34],
[ 35, 36, 37, 38, 39],
[ 40, 41, 42, 43, 44],
[ 45, 46, 47, 48, 49]],
[[600, 601, 602, 603, 604],
[605, 606, 607, 608, 609],
[610, 611, 612, 613, 614],
[615, 616, 617, 618, 619],
[620, 621, 622, 623, 624]],
[[ 50, 51, 52, 53, 54],
[ 55, 56, 57, 58, 59],
[ 60, 61, 62, 63, 64],
[ 65, 66, 67, 68, 69],
[ 70, 71, 72, 73, 74]]])
Resize an array padded with elements from itself:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: a_6 = a_3[0]
In[]: a_6
Out[]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
In[]: np.resize(a_6, (5,3))
Out[]:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 0],
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 0, 1],
[2, 3, 4]])
In[]: np.resize(a_6, (2, 5, 5))
Out[]:
array([[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]])
In[]: np.resize(a_3, (3,5,5))
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]],
[[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]],
[[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]])
Resize an array padded with zeros:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: a_3.resize((3, 3), refcheck=False)
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
In[]: a_3.resize((5, 6), refcheck=False)
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 20, 21, 22],
[23, 24, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
In[]: a_3.resize((10, 10), refcheck=False)
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
In[]: a_3.resize((3, 5, 10), refcheck=False)
In[]: a_3
Out[]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
[[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]])
Trim leading or trailing zeros from an array:
#
Trim leading or trailing zeros from a 1d array with np.trim_zeros(): (##)
In[]: a_6 = np.array([0,0,0,1,2,5,8,0])
In[]: np.trim_zeros(a_6, trim="f")
Out[]: array([1, 2, 5, 8, 0])
In[]: np.trim_zeros(a_6, trim="b")
Out[]: array([0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 5, 8])
In[]: np.trim_zeros(a_6, trim="fb")
Out[]: array([1, 2, 5, 8])
Flip an array on a specific axis:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.flip(a_3)
Out[]:
array([[24, 23, 22, 21, 20],
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10],
[ 9, 8, 7, 6, 5],
[ 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]])
In[]: np.flip(a_3, axis=0)
Out[]:
array([[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]])
In[]: np.flip(a_3, axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[ 4, 3, 2, 1, 0],
[ 9, 8, 7, 6, 5],
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10],
[24, 23, 22, 21, 20]])
Rotate an array:
#
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.roll(a_3, shift=3, axis=1)
Out[]:
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 0, 1],
[ 7, 8, 9, 5, 6],
[12, 13, 14, 10, 11],
[22, 23, 24, 20, 21]])
In[]: np.roll(a_3, shift=1, axis=0)
Out[]:
array([[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])
In[]: np.roll(a_3, shift=1, axis=None)
Out[]:
array([[24, 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 20, 21, 22, 23]])
#alternatively by 90 degrees
In[]: a_3 = array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])
In[]: np.rot90(a_3, k=1, axes=(0,1))
Out[]:
array([[ 4, 9, 14, 24],
[ 3, 8, 13, 23],
[ 2, 7, 12, 22],
[ 1, 6, 11, 21],
[ 0, 5, 10, 20]])
In[]: np.rot90(a_3, k=2, axes=(0,1))
Out[]: array([[24, 23, 22, 21, 20],
[14, 13, 12, 11, 10],
[ 9, 8, 7, 6, 5],
[ 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]])
In[]: np.rot90(a_3, k=3, axes=(0,1))
Out[]:
array([[20, 10, 5, 0],
[21, 11, 6, 1],
[22, 12, 7, 2],
[23, 13, 8, 3],
[24, 14, 9, 4]])
Return all unique items in an array:
#
In[]: a_9 = np.array([ 2, 2, 2, 23, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 23])
In[]: np.unique(a_9)
Out[]: array([ 1, 2, 3, 23])
String Array Methods
Arrays with string data are used almost exactly like Python lists. Although, arrays are faster and more efficient.
Convert a Python list to Numpy array:
#
In[]: s_1 = ['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.']
In[]: s_1a = np.asarray(s_1)
In[]: s_1a
Out[]: array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: s_1a.shape
Out[]: (9,)
Combine items in two arrays of the same shape:
#
In[]: s_a1 = array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: s_a2 = array(['This', 'is', 'an', 'array', 'of', 'string', 'data', 'right', 'here'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.add(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]:
array(['TheThis', 'rainis', 'inan', 'spainarray', 'staysof',
'mainlystring', 'indata', 'theright', 'plain.here'], dtype='<U12')
Multiply words by the integers in another array:
#
In[]: s_a1 = array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: s_m1 = np.arange(0,9)
In[]: np.char.multiply(s_1a, s_m1)
Out[]: array(['', 'rain', 'inin', 'spainspainspain', 'staysstaysstaysstays',
'mainlymainlymainlymainlymainly', 'inininininin',
'thethethethethethethe',
'plain.plain.plain.plain.plain.plain.plain.plain.'], dtype='<U48')
Change case of the font in each item on numpy array:
In[]: s_a1 = array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
#Capitolize the first letter of each word
In[]: np.char.capitalize(s_a1)
Out[]: array(['The', 'Rain', 'In', 'Spain', 'Stays', 'Mainly', 'In', 'The', 'Plain.'], dtype='<U6')
#uppercase each item
In[]: np.char.upper(s_a1)
Out[]: array(['THE', 'RAIN', 'IN', 'SPAIN', 'STAYS', 'MAINLY', 'IN', 'THE',
'PLAIN.'], dtype='<U6')
#lowercase each item
In[]: np.char.lower(s_a1)
Out[]: array(['the', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the',
'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
Pad each item with specific character:
#
In[]: s_a1 = array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
#pad items center
In[]: np.char.center(s_a1, width=12, fillchar='*')
Out[]:
array(['****The*****', '****rain****', '*****in*****', '***spain****',
'***stays****', '***mainly***', '*****in*****', '****the*****',
'***plain.***'], dtype='<U12')
#pad items justified right
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
Out[]: np.char.ljust(s_a1, width=10, fillchar='*')
In[]:
array(['The*******', 'rain******', 'in********', 'spain*****',
'stays*****', 'mainly****', 'in********', 'the*******',
'plain.****'], dtype='<U10')
#pad items justified left
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.rjust(s_a1, width=10, fillchar="*")
Out[]:
array(['*******The', '******rain', '********in', '*****spain',
'*****stays', '****mainly', '********in', '*******the',
'****plain.'], dtype='<U10')
Join characters into each item:
#
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.join(s_a1, 'ZQV')
Out[]:
array(['ZTheQTheV', 'ZrainQrainV', 'ZinQinV', 'ZspainQspainV',
'ZstaysQstaysV', 'ZmainlyQmainlyV', 'ZinQinV', 'ZtheQtheV',
'Zplain.Qplain.V'], dtype='<U15')
Strip specified leading characters:
#
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.lstrip(s_a1, chars='Tsmir')
Out[]:
array(['he', 'ain', 'n', 'pain', 'tays', 'ainly', 'n', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
Replace specified characters:
#
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.replace(s_a1, 'a', 'Z', count=None)
Out[]:
array(['The', 'rZin', 'in', 'spZin', 'stZys', 'mZinly', 'in', 'the', 'plZin.'], dtype='<U6')
Split Python list into an array:
#
In[]: s_1 = 'The rain in spain stays mainly in the plain.'
In[]: np.char.rsplit(s_a1, sep=None, maxsplit=None)
Out[]: array(list(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.']), dtype=object)
In[]: np.char.split(s_1, sep=None, maxsplit=3)
Out[]: array(list(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain stays mainly in the plain.']), dtype=object)
Remove specified string data:
#remove trailing characters
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.rstrip(s_a1, chars='s')
Out[]:
array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stay', 'mainly', 'in', 'the',
'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
#remove trailing or leading characters
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: np.char.strip(s_a1, 'rsmn.')
Out[]: array(['The', 'ai', 'i', 'pai', 'tay', 'ainly', 'i', 'the', 'plai'], dtype='<U6')
Comparison operators to each item between two equally sized string arrays:
#arrays to compare
In[]: s_a1 = np.array(['The', 'rain', 'in', 'spain', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'plain.'], dtype='<U6')
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'rain', 'in', 'california', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'north'])
#compare character by character with specific comparison operator
In[]: np.char.compare_chararrays(s_a1, s_a2, cmp='!=', rstrip=False)
Out[]: array([ True, False, False, True, False, False, True, False, True])
#s_a1 equal to s_a2
In[]: np.char.equal(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([False, True, True, False, True, True, False, True, False])
#s_a1 equal to s_a2
In[]: np.char.not_equal(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([ True, False, False, True, False, False, True, False, True])
#s_a1 item length less than s_a2
In[]: np.char.less(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([ True, False, False, False, False, False, True, False, False])
#s_a1 item length less than or item equal to s_a2
In[]: np.char.less_equal(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([ True, True, True, False, True, True, True, True, False])
#s_a1 item length greater than s_a2
In[]: np.char.greater(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([False, False, False, True, False, False, False, False, True])
#s_a1 item length greater than or equal to s_a2
In[]: np.char.greater_equal(s_a1, s_a2)
Out[]: array([False, True, True, True, True, True, False, True, True])
Return boolean for item ends with:
#
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'rain', 'in', 'california', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'north'])
In[]: np.char.endswith(s_a2, suffix='nia', start=0, end=None)
Out[]: array([False, False, False, True, False, False, False, False, False])
Return the index of a substring if it occurs in an item:
#
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'rain', 'in', 'california', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'north'])
In[]: np.char.find(s_a2, sub='nia', start=0, end=None)
Out[]: array([-1, -1, -1, 7, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1])
Truth value where items start with specific characters:
#
In[]: sa3 = np.array(['the', 'Calif9.9ornia', '8', 'WRITE', 'MAINLY', 'north', 1.25, 69])
In[]: np.char.startswith(sa3, prefix='nor', start=0, end=None)
Out[]: array([False, False, False, False, False, True, False, False])
Return the truth value of strings containing digits:
#
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'r699ain', 'in', 'calif99ornia', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'north'])
In[]: np.char.isalpha(s_a2)
Out[]: array([ True, False, True, False, True, True, True, True, True])
Truth value for items alphebetical or numeric:
#
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'r699ain', 'in', 'calif99ornia', 'stays', 'mainly', 'in', 'the', 'north', ' '])
In[]: np.char.isalnum(s_a2)
Out[]: array([ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, False])
Truth value for items that are only integers:
#
In[]: s_a2 = np.array(['the', 'r699ain', 'in', 'calif9.9ornia', '8', 'stays', 'mainly', 'north', 1.25, 69])
In[]: np.char.isdigit(s_a2)
Out[]: array([False, False, False, False, True, False, False, False, False, True])
Basic Imaging Methods
Here is a really basic example of how Numpy can convert an image to an array. I'll use
a dog picture from the Stanford Dogs dataset which can be used for AI testing and training.
It's open source and you can download it here.
This actually highlights one of the more difficult parts of working with data—at least from
what I have noticed is data collection can be difficult.
So here is our image:
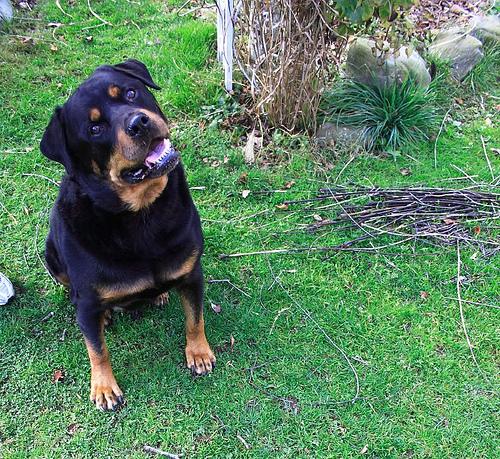

Image to array method 1:
#
In[]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
In[]: import matplotlib.image as mpimg
In[]: curious_rotty_1 = mpimg.imread('Path\To\File\n02106550_12828.jpg')
#Now we can call the array and see it as a numpy array
In[]: curious_rotty_1
Out[]:
array([[[133, 153, 204],
[146, 167, 220],
[160, 181, 236],
...,
[207, 226, 198],
[200, 218, 196],
[182, 198, 187]],
[[153, 173, 224],
[152, 174, 224],
[154, 175, 230],
...,
[186, 221, 181],
[177, 211, 178],
[161, 193, 169]],
[[173, 193, 243],
[166, 188, 238],
[163, 184, 237],
...,
[120, 173, 131],
[124, 176, 138],
[129, 180, 149]],
...,
[[175, 198, 170],
[164, 190, 155],
[196, 229, 182],
...,
[ 52, 134, 62],
[ 50, 132, 60],
[104, 186, 114]],
[[194, 212, 188],
[242, 255, 234],
[205, 237, 190],
...,
[ 70, 145, 76],
[106, 181, 112],
[135, 210, 141]],
[[136, 149, 129],
[118, 137, 109],
[113, 142, 98],
...,
[138, 207, 142],
[124, 193, 128],
[112, 181, 116]]], dtype=uint8)
#you can experiment with this and then view the image by calling
In[]: plt.imshow(curious_rotty_1)
#the image will plot
Image to array method 2:
#
In[]: Import numpy as np
In[]: import PIL
In[]: from PIL import Image
In[]: curious_rotty_2 = PIL.Image.open(r"Path\To\File\n02106550_12828.jpg")
#Now we can call the array and see it as a numpy array with np.asarray()
In[]: np.asarray(curious_rotty_1)
Out[]:
array([[[133, 153, 204],
[146, 167, 220],
[160, 181, 236],
...,
[207, 226, 198],
[200, 218, 196],
[182, 198, 187]],
[[153, 173, 224],
[152, 174, 224],
[154, 175, 230],
...,
[186, 221, 181],
[177, 211, 178],
[161, 193, 169]],
[[173, 193, 243],
[166, 188, 238],
[163, 184, 237],
...,
[120, 173, 131],
[124, 176, 138],
[129, 180, 149]],
...,
[[175, 198, 170],
[164, 190, 155],
[196, 229, 182],
...,
[ 52, 134, 62],
[ 50, 132, 60],
[104, 186, 114]],
[[194, 212, 188],
[242, 255, 234],
[205, 237, 190],
...,
[ 70, 145, 76],
[106, 181, 112],
[135, 210, 141]],
[[136, 149, 129],
[118, 137, 109],
[113, 142, 98],
...,
[138, 207, 142],
[124, 193, 128],
[112, 181, 116]]], dtype=uint8)
#this second method is already an image so to view it plot it with matplotlib
In[]: plt.imshow(curious_rotty_2)
#the image will plot